Symptoms and objective signs of peripheral sensory neuropathy in POTS and correlations to gastrointestinal symptoms
- PMID: 40608783
- PMCID: PMC12225795
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0327549
Symptoms and objective signs of peripheral sensory neuropathy in POTS and correlations to gastrointestinal symptoms
Abstract
Aim: Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) is a disorder with cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction where multiple and variable symptoms are common, including those from the peripheral and enteric nervous systems. We aimed to investigate subjective and objective signs of small and large fiber neuropathy in a Swedish POTS cohort compared with healthy controls. Secondly, we wanted to examine potential associations between gastrointestinal symptoms and neuropathy signs in POTS.
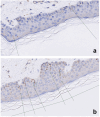
Methods: Forty-three patients with POTS (93% female) and 54 healthy controls (76% female) were included in the study. All participants completed a questionnaire including modified neuropathy symptoms score (NSS) and irritable bowel syndrome severity scoring system (IBS-SSS) for gastrointestinal evaluation. Small nerve fibers were investigated by assessing the intraepidermal nerve fiber density (IENFD). Large nerve fiber function was examined through pinprick and vibration perception thresholds (VPTs), using neurothesiometry and multi-frequency vibrometry (MFV). The patients were classified as "High NSS" and "High IBS-SSS" if their total NSS vs. IBS-SSS were above median levels in POTS.
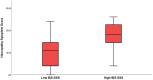
Results: Peripheral sensory and gastrointestinal symptoms were more prevalent and severe in POTS than in controls. Median VPTs were normal and IENFDs were comparable between POTS and controls (2.26 [1.62-3.08] vs. 1.63 [0.73-2.68] fibers/mm; p = 0.108). The patients with "high NSS" had slightly higher VPTs measured by MFV, although within normal ranges, compared to patients with "low NSS". The patients within the "high IBS-SSS" group had higher NSS (18.0 [14.3-22.8] vs. 11.0 [4.0-15.0]; p = 0.002) compared to patients with low total IBS-SSS.
Conclusion: Symptoms of peripheral and enteric neuropathy are common in POTS but no solid evidence was found regarding functional or morphological signs of small or large fiber neuropathy. Neuropathic and gastrointestinal symptoms were closely associated within POTS.
Copyright: © 2025 Ekman et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AGA Clinical Practice Update on GI Manifestations and Autonomic or Immune Dysfunction in Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome: Expert Review.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Jul;23(8):1291-1302. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2025.02.015. Epub 2025 May 19. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 40387691 Review.
-
Physical activity for treatment of irritable bowel syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jun 29;6(6):CD011497. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011497.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35766861 Free PMC article.
-
Small fiber neuropathy in children, adolescents, and young adults with chronic orthostatic intolerance and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome: A retrospective study.Auton Neurosci. 2024 Jun;253:103163. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2024.103163. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Auton Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38537312
-
A low FODMAP diet plus traditional dietary advice versus a low-carbohydrate diet versus pharmacological treatment in irritable bowel syndrome (CARIBS): a single-centre, single-blind, randomised controlled trial.Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jun;9(6):507-520. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(24)00045-1. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38643782 Clinical Trial.
-
Self-reported symptom burden in postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS): A narrative review of observational and interventional studies.Auton Neurosci. 2023 Jan;244:103052. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2022.103052. Epub 2022 Nov 18. Auton Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36525900
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

