Aedes aegypti ecology and dengue infection in three agricultural areas of Côte d'Ivoire
- PMID: 40609054
- PMCID: PMC12303389
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0013255
Aedes aegypti ecology and dengue infection in three agricultural areas of Côte d'Ivoire
Abstract
Background: Over the last ten years, there has been an upsurge of dengue outbreaks in Côte d'Ivoire, with Aedes aegypti as the principal vector. The intensification of farming activities and the living conditions of local populations could lead to a proliferation of artificial breeding sites for Ae. aegypti, which would increase the risk of dengue transmission in rural areas. The present study characterised the habitats of Ae. aegypti larvae and assessed the risk of dengue transmission in three key agricultural areas of Côte d'Ivoire.
Methodology: Aedes aegypti (larvae, pupae and adults) were collected from human dwellings in three key agricultural areas of Côte d'Ivoire during the rainy season. Risk indices including traditional Stegomyia indices and pupal indices were estimated. RT-qPCR was used to detect DENV in the pools of Ae. aegypti.
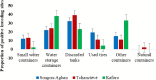
Principal findings: Aedes aegypti was the predominant species collected at the three locations. The predominant breeding sites were discarded tanks in Songon-Agban and Tchanctévè, and water storage tanks in Kaforo. High Stegomyia indices (house indices >5% and/or Breteau indices >20) and pupal indices (PIH [0.8 - 2.2] and PIP [0.1 - 0.4]) were recorded in all three sites, suggesting a high risk of dengue transmission. DENV-3 was detected in 1/96 (3.6%) pools of Ae. aegypti collected as immature stages in Songon-Agban with a minimum infection rate (MIR) of 1.9 per 1000 mosquitoes.
Conclusions/significance: The findings of this study indicated a high entomological risk of dengue across the three agricultural sites. It is important that the potential for transovarial transmission of DENV-3 in Ae. aegypti is considered when formulating control strategies against this vector in Côte d'Ivoire.
Copyright: © 2025 Kadjo et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Msimang V, Kemp A, van Vuren PJ, Weyer J, Paweska J. Increased importation of dengue cases into South Africa: a risk for establishment of local endemicity? National Institute for Communicable Diseases. 2018;16.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

