Insights into ancestral diversity in Parkinson's disease risk: a comparative assessment of polygenic risk scores
- PMID: 40610451
- PMCID: PMC12229533
- DOI: 10.1038/s41531-025-00967-4
Insights into ancestral diversity in Parkinson's disease risk: a comparative assessment of polygenic risk scores
Abstract
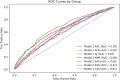
Risk prediction models play a crucial role in advancing healthcare by enabling early detection and supporting personalized medicine. Nonetheless, polygenic risk scores (PRS) for Parkinson's disease (PD) have not been extensively studied across diverse populations, contributing to health disparities. In this study, we constructed 105 PRS using individual-level data from seven ancestries and compared two different models. Model 1 was based on the cumulative effect of 90 known European PD risk variants, weighted by summary statistics from four independent ancestries (European, East Asian, Latino/Admixed American, and African/Admixed). Model 2 leveraged multi-ancestry summary statistics using a p-value thresholding approach to improve prediction across diverse populations. Our findings provide a comprehensive assessment of PRS performance across ancestries and highlight the limitations of a "one-size-fits-all" approach to genetic risk prediction. We observed variability in predictive performance between models, underscoring the need for larger sample sizes and ancestry-specific approaches to enhance accuracy. These results establish a foundation for future research aimed at improving generalizability in genetic risk prediction for PD.
© 2025. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: M.A.N. and H.L.’s participation in this project was part of a competitive contract awarded to Data Tecnica International LLC by the National Institutes of Health to support open science research. M.A.N. also currently serves on the scientific advisory board for Character Bio Inc. and Neuron23 Inc. L.N.K. and K.H. are employed by and hold stock or stock options in 23andMe, Inc. A.S. serves as an Associate Editor for NPJ Parkinson’s Disease.
Figures




Update of
-
Insights into Ancestral Diversity in Parkinsons Disease Risk: A Comparative Assessment of Polygenic Risk Scores.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 9:2023.11.28.23299090. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.28.23299090. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2025 Jul 3;11(1):201. doi: 10.1038/s41531-025-00967-4. PMID: 38076954 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

