Epidemiology and future trend predictions of ischemic stroke based on the global burden of disease study 1990-2021
- PMID: 40610700
- PMCID: PMC12229500
- DOI: 10.1038/s43856-025-00939-y
Epidemiology and future trend predictions of ischemic stroke based on the global burden of disease study 1990-2021
Abstract
Background: Visualizing the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study (GBD) 2021 and predicting future disease burdens at global, regional, and national levels can help health policymakers develop evidence-based ischemic stroke (IS) prevention and cure strategies.
Methods: We stratify epidemiological parameters by sex, age, the World Bank's classification of economies, and sociodemographic index (SDI) levels. We use frontier analysis to assess whether the burden of ischemic stroke (IS) in each country aligns with its level of economic development. We apply the Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) model and the Bayesian age-period-cohort (BAPC) model to predict the burden of IS over the next 15 years.
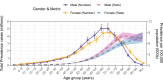
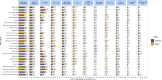
Results: Here we show that IS accounts for 69.9 million prevalent cases, 7.8 million incident cases, 3.6 million deaths, and 70.4 million DALYs in 2021. In men, the global DALY rate of IS increases up to age 90-94 years and then decreases; however, for women, the rate increases up to the oldest age group (≥95 years). Regionally, we find that the association between the SDI and the age-standardized DALY rate of IS starts relatively flat, with a small peak up to a sociodemographic index of about 0.7, and then declines rapidly. Factors contributing most to the DALY rates for IS are high systolic blood pressure, high LDL cholesterol, and air pollution.
Conclusions: The disease burden of IS in medium-high SDI countries is still high, which means we could not meet the Sustainable Development Goal targets by 2030. Countries should formulate prevention and control measures suitable for their national conditions based on risk factors.
Plain language summary
Ischemic stroke (IS) occurs when blood flow to part of the brain is reduced or stopped by a blood vessel becoming blocked. We assessed death, prevalence, mortality, disability, and risk factors related to people experiencing IS between 1990 and 2021 in 204 countries and territories and predicted how these might change in the future. Globally, IS accounted for 3.6 million deaths in 2021. Although the frequency of occurrences of IS and deaths due to IS has decreased over the past three decades, the absolute number of ISs is increasing as a result of population growth and population aging. The main risk factors include high systolic blood pressure, high low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and air pollution. Our data could be useful at the global, regional, and national levels to help health policymakers develop evidence-based IS prevention and care strategies.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Ferrari, A. J. et al. Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet403, 2133–2161 (2024). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ding, Q. et al. Global, regional, and national burden of ischemic stroke, 1990–2019. Neurology98, e279–e290 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Bennett, D. A. et al. The global burden of ischemic stroke: findings of the GBD 2010 study. Glob. Heart9, 107–112 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Krishnamurthi, R. V. et al. Stroke prevalence, mortality and disability—adjusted life years in children and youth aged 0–19 years: data from the global and regional burden of stroke 2013. Neuroepidemiology45, 177–189 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Krishnamurthi, R. V. et al. Stroke prevalence, mortality and disability-adjusted life years in adults aged 20–64 years in 1990–2013: data from the global burden of disease 2013 study. Neuroepidemiology45, 190–202 (2015). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

