A novel modulator of IL-6R prevents inflammation-induced preterm birth and improves newborn outcome
- PMID: 40610814
- PMCID: PMC12340070
- DOI: 10.1038/s44321-025-00257-9
A novel modulator of IL-6R prevents inflammation-induced preterm birth and improves newborn outcome
Abstract
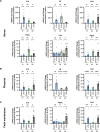
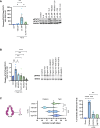
Preterm birth (PTB) is a major cause of neonatal mortality and morbidity. Evidence supports a determinant role for interleukin-6 (IL-6) in the pathophysiology of PTB. Our group developed a small peptide, HSJ633, that antagonizes the interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R). Binding assays performed on HEK-Blue IL-6 cells reveal that HSJ633 appears to bind to IL-6R on a site remote from the IL-6 binding domain. Concordantly, HSJ633 selectively inhibits STAT3 phosphorylation while preserving the activation of cytoprotective AKT, p38, and ERK 1/2. In vivo, in a murine model of LPS-induced PTB, HSJ633 reduces inflammation in gestational and fetal tissues, preserves the integrity of fetal organs, and improves the survival of neonatal progeny when administered before and after the induction of labor by an inflammatory stimulus. Relevantly, the pharmacological inhibition of STAT3 in mice is sufficient to prevent PTB. Findings reveal first-in-class efficacy of a small peptide inhibitor of IL-6R, namely HSJ633, in impeding the inflammatory cascade associated with PTB and mitigating adverse neonatal outcomes.
Keywords: Inflammation; Interleukin-6; Neonatal Mortality; Non-competitive Modulator; Preterm Birth.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

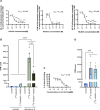
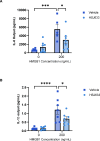
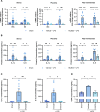
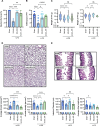
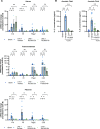

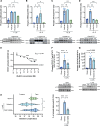
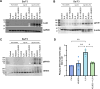


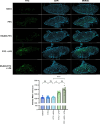
References
-
- Arntzen KJ, Kjøllesdal AM, Halgunset J, Vatten L, Austgulen R (1998) TNF, IL-1, IL-6, IL-8 and soluble TNF receptors in relation to chorioamnionitis and premature labor. J Perinat Med 26:17–26 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

