Green HPLC strategy for quantification of carvedilol and hydrochlorothiazide in cardiac medications with in-vitro dissolution kinetics and impurity profiling
- PMID: 40611289
- PMCID: PMC12224793
- DOI: 10.1186/s13065-025-01559-2
Green HPLC strategy for quantification of carvedilol and hydrochlorothiazide in cardiac medications with in-vitro dissolution kinetics and impurity profiling
Abstract
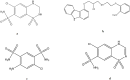
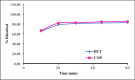
The introduction of new pharmaceutical formulations necessitates the development of a trustworthy analytical approach capable of quantifying active ingredients in various quality control procedures. A fixed dosage combination of carvedilol (CAR) and hydrochlorothiazide (HCT) has been introduced to treat hypertension with potential recommendation for diabetic patients. Ahigh-performance liquid chromatographic methodology, designed to be ecologically sustainable while maintaining high precision and accuracy, was established. This approach can simultaneously determine both drugs in their pure forms, and dosage form, along with separation and quantification of potential hydrochlorothiazide related impurities; salamide (DSA) and chlorothiazide (CT). Successful separation was performed using YMC®Triart-Phenyl analytical column via gradient elution employing 0.1% formic acid alongside ethanol at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min, coupled with photodiode array detection at 254.0 nm. Linearity was obtained across the concentration ranges of 0.1 to 100.0 µg/mL for HCT and CAR and 0.05 to 10.0 µg/mL for DSA and CT. The suggested chromatographic methodology can estimate HCT and CAR in different real samples. Additionally, it facilitates the concurrent monitoring of their dissolution profiles. The studied method's performance was validated in adherence to the guidelines set by the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH). Moreover, its ecological sustainability as well as applicability profile was further affirmed via diverse greenness, blueness, and whiteness assessment tools and compared among official and other reported procedures. In addition, the recently introduced Carbon Footprint Reduction Index tool has been implemented to assess the suggested method with an emphasis on estimating CO2 emissions. In general, the suggested methodology proves to be effective for conducting the quality control examination of raw forms and commercially accessible preparations.
Keywords: Blueness; Carbon footprint; Cardiac pharmaceutical formulations; Carvedilol; Click analytical chemistry; Dissolution testing; Greenness profile; Hydrochlorothiazide; Impurity profiling; Whiteness assessment..
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Gałuszka A, Migaszewski Z, Namieśnik J. The 12 principles of green analytical chemistry and the SIGNIFICANCE mnemonic of green analytical practices. TRAC Trends Anal Chem. 2013;50:78–84.
-
- Kurowska-Susdorf A, Zwierżdżyński M, Bevanda AM, Talić S, Ivanković A, Płotka-Wasylka J. Green analytical chemistry: social dimension and teaching. TRAC Trends Anal Chem. 2019;111:185–96.
-
- Nowak PM, Wietecha-Posłuszny R, Pawliszyn J. White analytical chemistry: an approach to reconcile the principles of green analytical chemistry and functionality. TRAC Trends Anal Chem. 2021;138:116223.
-
- Manousi N, Wojnowski W, Płotka-Wasylka J, Samanidou V. Blue applicability grade index (BAGI) and software: a new tool for the evaluation of method practicality. Green Chem. 2023;25(19):7598–604.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
