PPP2CB aggravates atherosclerosis-related dyslipidemia via LOX-1/MAPK/ERK signaling pathway
- PMID: 40611318
- PMCID: PMC12224689
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-025-02647-x
PPP2CB aggravates atherosclerosis-related dyslipidemia via LOX-1/MAPK/ERK signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Dyslipidemia has been extensively documented as a key driver of cardiovascular pathology. Regulating lipid homeostasis holds promise for treating atherosclerosis (AS). Although the protein phosphatase 2 catalytic subunit beta (PPP2CB) is involved in post-transcriptional gene regulation, its role in AS-associated dyslipidemia is not well understood.
Methods: The study included both human participants and animal models. The following techniques were employed: cell culture, extraction of exosomes, preparation of pooled hyperlipidemic serum (HS), transfection, western blotting, immunofluorescence staining, quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), co-immunoprecipitation, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) uptake assay, biochemical assays, assessment of aortic atherosclerotic lesions, as well as statistical analysis.
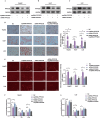
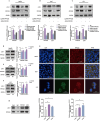
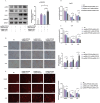
Results: This study identified a marked upregulation of PPP2CB expression in peripheral blood leukocytes of AS patients, artery plaque of ApoE-/- mice given a high-fat diet, and hepatic cells exposed to hyperlipidemic stimuli. Overexpression of PPP2CB in hepatic cells exacerbated lipid accumulation and low-density lipoprotein uptake, whereas silencing PPP2CB mitigated this effect. Immunofluorescence co-localization and co-immunoprecipitation analysis confirmed a direct interaction between PPP2CB and lectin-like oxidized LDL receptor-1 (LOX-1). Notably, PPP2CB manipulation disrupted hyperlipidemia-induced LOX-1 expression. Additionally, PPP2CB-mediated lipid dysregulation was linked to the activation of the LOX-1/ mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/ extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling cascade.
Conclusions: These results unveil PPP2CB as a novel lipid regulator in the progression of pathological AS and highlight its involvement in signaling regulation during abnormal lipid metabolism. PPP2CB could be considered a promising candidate for biomarker development and therapeutic intervention in AS.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Dyslipidemia; LOX-1; Liver cells; PPP2CB.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval consent to participate: The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Taihe Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to enrollment. The animal experiments were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Hubei University of Medicine. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

