Distinctive Features of Rotational Thromboelastometry in Patients with Infective Endocarditis Undergoing on-Pump Cardiac Surgery: A Retrospective Propensity Score-matched Observational Study
- PMID: 40611626
- PMCID: PMC12227918
- DOI: 10.1177/10760296251356205
Distinctive Features of Rotational Thromboelastometry in Patients with Infective Endocarditis Undergoing on-Pump Cardiac Surgery: A Retrospective Propensity Score-matched Observational Study
Abstract
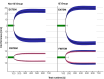
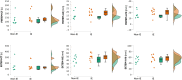
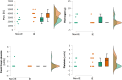
BackgroundThe haemostatic system plays a role in development of valvular vegetations and systemic activation of coagulation, contributing to both thrombosis and consumption coagulopathy. Patients with infective endocarditis undergoing valvular surgery pose unique challenges to the surgical team. Rotational thromboelastometry (ROTEM), a point-of-care viscoelastic clotting test, can help assess coagulation and guide therapy. This retrospective propensity score-matched study explores ROTEM's distinctive features in endocarditis patients compared to others undergoing cardiac surgery.Materials and MethodsA retrospective analysis was performed on patients undergoing valvular surgery between May 31, 2022, and August 31, 2024. ROTEM assessments were conducted during extracorporeal circulation and post-heparin reversal. The study group consisted of patients with endocarditis, while propensity score matching created a control group of patients without endocarditis. The primary outcome was on-pump ROTEM results; secondary outcomes included utilisation of red blood cells (pRBC), fibrinogen concentrate (FC), prothrombin complex concentrate (PCC), fresh frozen plasma (FFP), and platelets.ResultsIn both groups (23 patients each), endocarditis patients had prolonged EXTEM clotting times (136 vs 96 s, P = .001) and higher FIBTEM-A5 clot firmness (19 vs 13 mm, P = .012). They required more PCC (3000 vs 2500 units, P = .014), while transfusions of platelets (P = .281), FFP (P = 1.000), and FC (P = .109) did not differ significantly.ConclusionEndocarditis patients demonstrate distinct viscoelastic profiles with prolonged clotting times and increased clot firmness, necessitating greater PCC supplementation. Further research is warranted to optimise ROTEM target values to balance bleeding and thrombotic risks.
Keywords: ROTEM; coagulation; endocarditis; patient blood management; viscoelastic tests.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe authors declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: During the preparation of this study, the authors used DeepL to improve readability and language. After using this tool, the authors reviewed and edited the content as needed, and took full responsibility for the content of the publication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thromboelastography (TEG) or thromboelastometry (ROTEM) to monitor haemostatic treatment versus usual care in adults or children with bleeding.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 22;2016(8):CD007871. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007871.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27552162 Free PMC article.
-
Rotational thromboelastometry (ROTEM) in pediatric intensive care: A single center experience.Transfus Apher Sci. 2025 Aug;64(4):104194. doi: 10.1016/j.transci.2025.104194. Epub 2025 Jun 21. Transfus Apher Sci. 2025. PMID: 40578147
-
Pre-operative reference ranges for ROTEM® sigma in patients undergoing cardiac surgery: a secondary analysis of two prospective trial cohorts.Anaesthesia. 2025 Aug;80(8):935-945. doi: 10.1111/anae.16608. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Anaesthesia. 2025. PMID: 40230308 Free PMC article.
-
Prothrombin complex concentrate in cardiac surgery for the treatment of coagulopathic bleeding.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 21;11(11):CD013551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013551.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36408876 Free PMC article.
-
Fibrinolytic activity in infants undergoing cardiac surgery on cardiopulmonary bypass with routine tranexamic acid: A prospective cohort substudy within the FIBrinogen CONcentrate randomised control trial.Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2025 May 1;42(5):389-397. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0000000000002124. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2025. PMID: 39895347 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Xiong Y, Van Wamel W, Nast CC, Yeaman MR, Cheung AL, Bayer AS. Activation and transcriptional interaction between agr RNAII and RNAIII in Staphylococcus aureus in vitro and in an experimental endocarditis model. J Infect Dis. 2002;186(5):668–677. - PubMed
-
- Liesenborghs L, Meyers S, Vanassche T, Verhamme P. Coagulation: At the heart of infective endocarditis. J Thromb Haemost JTH. 2020;18(5):995–1008. - PubMed
-
- Ekdahl KN, Teramura Y, Hamad OA, et al. Dangerous liaisons: Complement, coagulation, and kallikrein/kinin cross-talk act as a linchpin in the events leading to thromboinflammation. Immunol Rev. 2016;274(1):245–269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

