This is a preprint.
Identification of a conserved RNA structure in the TNFRSF1A 3'UTR: Implications for post-transcriptional regulation
- PMID: 40611903
- PMCID: PMC12224534
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.06.18.660452
Identification of a conserved RNA structure in the TNFRSF1A 3'UTR: Implications for post-transcriptional regulation
Abstract
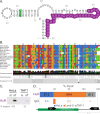
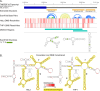
Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily 1A gene (TNFRSF1A) encodes the TNFR1 protein, a critical regulator of inflammation implicated in various diseases. Using ScanFold with the Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV) GUI, we identified novel RNA structural elements within the TNFRSF1A gene. Focusing on the 3'UTR, these structures were characterized using reporter assays and targeted DMS-MaPseq. We identified a structured region that may play a role in regulating TNFR1 translation and that was also found to associate with HuR, a key regulatory RNA-binding protein. These findings provide a framework for identifying and characterizing potential functional RNA structures in therapeutically relevant genes, suggesting a new layer of post-transcriptional regulation for TNFR1 expression.
Keywords: DMS-MaPseq; HuR; RNA; TNFR1; TNFRSF1A; inflammation; structure probing; translational efficiency; untranslated region (UTR).
Figures


References
-
- Baker SJ, Reddy EP. Transducers of life and death: TNF receptor superfamily and associated proteins. Oncogene. 1996;12(1):1–9. Epub 1996/01/04. - PubMed
-
- Caminero A, Comabella M, Montalban X. Role of tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α and TNFRSF1 R92Q mutation in the pathogenesis of TNF receptor-associated periodic syndrome and multiple sclerosis. Clinical & Experimental Immunology. 2011;166(3):338–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04484.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
