PPP1R12B inhibits cell proliferation by inducing G0/G1 phase arrest via PAK2/β-catenin axis in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 40612101
- PMCID: PMC12222077
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1621705
PPP1R12B inhibits cell proliferation by inducing G0/G1 phase arrest via PAK2/β-catenin axis in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
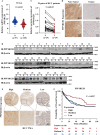
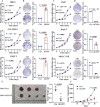
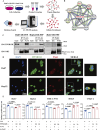
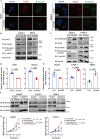
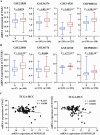
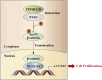
Protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 12B (PPP1R12B) is a regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 1. While our previous study identified the inhibitory role of PPP1R12B in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the precise molecular mechanisms underlying its anti-proliferative effects remain unclear. Herein, we demonstrated that PPP1R12B expression is significantly downregulated in HCC tissues and serves as an independent prognostic marker for favorable patient outcomes. Additionally, overexpression and silence of PPP1R12B experiments showed that PPP1R12B overexpression restricted cell proliferation and colony formation in vitro, and inhibited xenografted tumor growth in vivo, while its knockdown had opposite effects. Mechanistically, PPP1R12B could interact with p21-activated kinase 2 (PAK2) to suppress β-catenin expression and phosphorylation at Ser675, thereby impeding its nuclear translocation and subsequent transcriptional activation of Cyclin D1. This cascade culminated in G0/G1 phase cell cycle arrest. Furthermore, analysis of TCGA-HCC datasets confirmed inverse correlations between PPP1R12B and PAK2 or CTNNB1 (β-catenin) expression. Collectively, our findings elucidated a novel tumor-suppressive role of PPP1R12B in HCC through modulation of the PAK2/β-catenin/Cyclin D1 axis.
Keywords: PAK2/β-catenin axis; PPP1R12B; cell cycle; cell proliferation; hepatocellular carcinoma.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Liu, Bai, Zhao, Wang, Bao, Bao, Shen, Lu, Xiong, Gu, Wang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nuclear factor IA-mediated transcriptional regulation of crystallin αB inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression.Mol Clin Oncol. 2025 Jun 20;23(2):72. doi: 10.3892/mco.2025.2867. eCollection 2025 Aug. Mol Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40599718 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying interferon-alpha-induced G0/G1 arrest: CKI-mediated regulation of G1 Cdk-complexes and activation of pocket proteins.Oncogene. 1999 May 6;18(18):2798-810. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202609. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10362250
-
NSUN6 Maintains BMPER Stability in an m5C-Dependent Manner to Suppress Cell Proliferation and Migration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Biol Cell. 2025 Jul;117(7):e70023. doi: 10.1111/boc.70023. Biol Cell. 2025. PMID: 40589169 Free PMC article.
-
Sun protection for preventing basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jul 25;7(7):CD011161. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011161.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27455163 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

