The Global Burden of Major Gastrointestinal Anomalies: A Global, Systematic Review of Gastrointestinal Anomaly Birth Prevalence
- PMID: 40612188
- PMCID: PMC12219495
- DOI: 10.1177/30502225251304582
The Global Burden of Major Gastrointestinal Anomalies: A Global, Systematic Review of Gastrointestinal Anomaly Birth Prevalence
Abstract
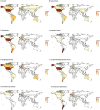
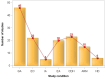
The burden of congenital gastrointestinal (GI) anomalies is poorly understood. The aim of this systematic review to assess the global prevalence of congenital gastrointestinal (GI) anomalies. We conducted a systematic review of global population-level birth prevalence of gastroschisis, omphalocele, intestinal atresia, esophageal atresia, congenital diaphragmatic hernia, Hirschsprung's disease, and anorectal malformation. We identified 103 studies from high and middle-income countries. Gastroschisis was the most reported condition. Studies reported geographic heterogeneity in gastroschisis, omphalocele, esophageal atresia, Hirschsprung's disease, congenital diaphragmatic hernia, and anorectal malformation prevalence. The prevalence of gastroschisis, omphalocele, and Hirschsprung's disease prevalence was reported to have increased over recent decades. Mean prevalence per 10 000 live and total births ranged from 2.1 to 4.4 cases and 1.4 to 3.6 per 10 000 live or total births, respectively. There is limited surveillance for congenital GI anomalies in LICs and potential temporal and geographic trends that need to be further investigated.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systematic Review of the Prevalence of Gastrointestinal Congenital Anomalies: A Global and Regional Review Protocol.Sage Open Pediatr. 2025 Mar 27;12:30502225251283177. doi: 10.1177/30502225251283177. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Sage Open Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40612197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Challenges of management and outcome of neonatal surgery in Africa: a systematic review.Pediatr Surg Int. 2016 Mar;32(3):291-9. doi: 10.1007/s00383-016-3861-x. Epub 2016 Jan 18. Pediatr Surg Int. 2016. PMID: 26783085
-
Antioxidants for male subfertility.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 4;5(5):CD007411. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007411.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35506389 Free PMC article.
-
Global birth prevalence of major congenital anomalies: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Public Health. 2025 Feb 4;25(1):449. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-21642-6. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39905325 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressants for pain management in adults with chronic pain: a network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(62):1-155. doi: 10.3310/MKRT2948. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367772 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Strengthening Emergency and Essential Surgical Care and Anaesthesia as a Component of Universal Health Coverage . 6 https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/253244 (2015).
-
- Kids Operating Room Global Report: The Unmet Need of Children’s Surgery in 2022 . 15 https://www.kidsor.org/our-work/research-and-impact/global-reports/ (2022).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources