Innovation of new Florescent-epitope technique for immune assay methods
- PMID: 40612260
- PMCID: PMC12226053
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mex.2025.103451
Innovation of new Florescent-epitope technique for immune assay methods
Abstract
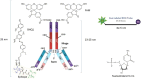
The proposed method, which utilizes a FAM fluorescent dye and a BHQ1 quencher complex for indirect analyte assessment through antigen-antibody reactions, represents a significant advancement in immune assay technology. By leveraging the unique physical properties of the FAM-BHQ1 complex, we achieve enhanced accuracy and efficiency in analyte quantification. The complex's fluorescence characteristics, along with its inherent stability and resistance to photobleaching, contribute to improved data reproducibility. Furthermore, the system's adaptability to multiplex assays allows for simultaneous detection of multiple analytes within a single reaction, significantly increasing throughput and reducing assay time. Favorable conditions enhance the method's performance, including a broad dynamic range and minimal background signal. The inherent advantages of this approach-increased sensitivity and specificity, coupled with streamlined workflow-promise to revolutionize immunological research and diagnostics. Implementing this FAM-BHQ1-based method will facilitate more precise and reliable detection and quantification of a broader range of analytes, leading to improved diagnostic accuracy and more effective therapeutic interventions.•Despite the importance of immune assays, these assays face challenges such as standardization, variability, and issues with sensitivity.•Our propose is the use of the FAM fluorescent day, which can attach to the Fc region of the antibody and BHQ1•This limitation is the time and number of epitope-to-paratope attachments.
Keywords: BHQ-1; Epitope-paratope reaction; FAM; Florescent dye; Immunoassay; Prob antibody.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Waner T., Mazar S., Keren-Kornblatt E. Application of a dot enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for evaluation of the immune status to canine parvovirus and distemper virus in adult dogs before revaccination. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2006;18(3):267–270. - PubMed
-
- Lin Y., Deng X., Shen N., Zhao L., Meng Q., Max J., et al. A flow cytometric assay for the expression of interferon gamma in T lymphocytes and its application in the study of EIAV-induced immune response] Wei. Sheng. Wu Xue Bao. 2008;48(6):800–805. - PubMed
-
- Noel G., DeKoter R.P., Wang Q., Hexley P., Ogle C.K. Optimization and application of a flow cytometric PU.1 assay for murine immune cells. J. Immunol. Methods. 2012;382(1–2):81–92. - PubMed
-
- Bessos H., Yule A. Direct comparisons between a radio-immune antiglobulin test, an enzyme-linked antiglobulin test, and a haemagglutination assay: application to the screening of anti-RBC sera and monoclonal antibodies. Vox. Sang. 1983;44(5):289–295. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

