Gait analysis in older adults with mild cognitive impairment: a bibliometric analysis of global trends, hotspots, and emerging frontiers
- PMID: 40612530
- PMCID: PMC12222084
- DOI: 10.3389/fragi.2025.1592464
Gait analysis in older adults with mild cognitive impairment: a bibliometric analysis of global trends, hotspots, and emerging frontiers
Abstract
Background: Gait analysis has emerged as a critical non-invasive tool for early identification and monitoring of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) in aging populations, particularly given its potential to predict dementia progression. This bibliometric analysis synthesizes two decades of research to map the evolution of gait analysis in MCI, identify interdisciplinary collaborations, and highlight emerging frontiers in MCI-related mobility research.
Methods: Literature related to gait analysis in MCI was retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection. The search spanned publications from 2005 to 2024 and was executed in a single search session on 15 December 2024. CiteSpace and VOSviewer software were used to analyze publications, authorship, institutional affiliations, journals, keywords, and cited references. Burst detection and timeline analyses of keywords and references were conducted to identify emerging trends and temporal patterns.
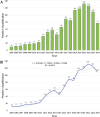
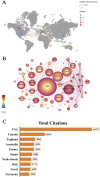
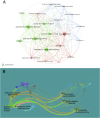
Results: A total of 1,223 articles were identified. Annual publication trends indicate sustained scholarly interest over the past 5 years. The United States contributed the most publications (392 articles, 32.05%), with Western University (Canada, 65 articles) as the leading institution. Journals publishing these studies primarily focus on Alzheimer's disease (AD), gerontology, and neurology, while prolific authors like Verghese J (USA) and Montero-odasso M(Canada) shaped the field's trajectory. Emerging research frontiers include dementia progression, AD, and Parkinson's disease, with 2024 priorities emphasizing "dual-task walking", "digital biomarkers" and "working groups". Additionally, validity and reliability assessments of gait analysis for MCI diagnosis and intervention represent a growing research trend.
Conclusion: This study provides a comprehensive overview of the current landscape, hotspots, and trends in gait analysis for MCI management. By delineating its transformation from a descriptive tool to a predictive framework, we highlight persistent challenges such as methodological heterogeneity and small sample sizes. However, advances in machine learning and multicenter collaborations present opportunities to standardize protocols. Future high-quality studies are expected to establish gait-derived biomarkers as clinically actionable tools in MCI stratification and therapeutic monitoring.
Keywords: bibliometric analysis; dementia; gait analysis; mild cognitive impairment; research hotspots.
Copyright © 2025 Zhong, Huang, Zou, Chen, Shen, He, Li, Liu and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Research status, hotspots and perspectives of artificial intelligence applied to pain management: a bibliometric and visual analysis.Updates Surg. 2025 Jun 28. doi: 10.1007/s13304-025-02296-w. Online ahead of print. Updates Surg. 2025. PMID: 40580377
-
Data-driven trends in critical care informatics: a bibliometric analysis of global collaborations using the MIMIC database (2004-2024).Comput Biol Med. 2025 Sep;195:110670. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2025.110670. Epub 2025 Jun 27. Comput Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 40580617
-
CSF tau and the CSF tau/ABeta ratio for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 22;3(3):CD010803. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010803.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28328043 Free PMC article.
-
Application of non-invasive imaging in myocardial infarction: a bibliometric analysis from January 2003 to December 2022.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025 Jul 1;15(7):6340-6359. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-878. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025. PMID: 40727351 Free PMC article.
-
A bibliometric analysis of research trends in mesenchymal stem cell therapy for neonatal bronchopulmonary dysplasia: 2004-2024.Front Pediatr. 2025 Jun 3;13:1558301. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1558301. eCollection 2025. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40530182 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

