Exploring the antimicrobial potential of Rosmarinus officinalis against urinary tract infection isolates in Amman, Jordan
- PMID: 40612734
- PMCID: PMC12218879
- DOI: 10.18502/ijm.v17i3.18829
Exploring the antimicrobial potential of Rosmarinus officinalis against urinary tract infection isolates in Amman, Jordan
Abstract
Background and objectives: The public health concern about urinary tract infections (UTIs) exists due to mounting antibiotic resistance rates. The antimicrobial properties of Rosmarinus officinalis create strong opportunities as an alternative therapeutic option. This study evaluated the antibacterial properties along with anti-biofilm behavior of rosemary extract against typical uropathogens.
Materials and methods: This study collected samples from 500 UTI isolates for its cross-sectional research. The antibacterial activity of rosemary extract underwent testing for its effects on Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterococcus faecalis, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa through combination tests with disk diffusion, MIC and MBC assays. Biofilm inhibition was assessed using the Tissue Culture Plate method with extract concentrations of 25, 50, and 100 µg/mL. Statistical analysis included one-way ANOVA, Tukey's post-hoc, and regression analysis.
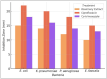
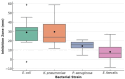
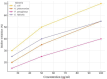
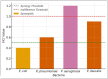
Results: The rosemary extract exhibited varying antibacterial effects, with inhibition zones ranging from 10 mm in E. faecalis to 16 mm in E. coli. MIC values were 4 mg/mL for E. coli and 32 mg/mL for E. faecalis, while MBC values ranged from 8 to 64 mg/mL. A 100 µg/mL concentration reduced E. coli biofilm formation by 70%. In checkerboard assays, rosemary extract enhanced antibiotic activity against E. coli and showed additive effects with K. pneumoniae and E. faecalis.
Conclusion: R. officinalis extract demonstrates promising antibacterial and anti-biofilm activities, suggesting potential as an adjunct UTI treatment, comparable to co-trimoxazole. Further research is recommended.
Keywords: Anti-bacterial agents; Biofilms; Drug resistance; Phytotherapy; Plant extracts; Rosmarinus; Urinary tract infections.
Copyright© 2025 The Authors. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Figures


References
-
- Al-Sereiti MR, Abu-Amer KM, Sen P. Pharmacology of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis Linn.) and its therapeutic potentials. Indian J Exp Biol 1999; 37: 124–130. - PubMed
-
- Banwo K, Olojede AO, Adesulu-Dahunsi AT, Verma DK, Thakur M, Tripathy S, et al. Functional importance of bioactive compounds of foods with potential health benefits: A review on recent trends. Food Biosci 2021; 43: 101320.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
