Kitlo hematopoietic stem cells exhibit distinct lymphoid-primed chromatin landscapes that enhance thymic reconstitution
- PMID: 40615375
- PMCID: PMC12227609
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-61125-1
Kitlo hematopoietic stem cells exhibit distinct lymphoid-primed chromatin landscapes that enhance thymic reconstitution
Abstract
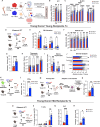
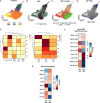
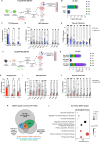
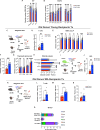
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) with multilineage potential are critical for T cell reconstitution after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT). The Kitlo HSC subset is enriched for multipotential precursors, but their T cell potential remains poorly characterized. Using a preclinical allo-HCT mouse model, we demonstrate that Kitlo HSCs provide superior thymic recovery and T cell reconstitution, resulting in improved immune responses to post-transplant infection. Kitlo HSCs with augmented bone marrow (BM) lymphopoiesis mitigate age-associated thymic alterations and enhance T cell recovery in middle-aged mice. Mechanistically, chromatin profiling reveals Kitlo HSCs exhibiting higher activity of lymphoid-specifying transcription factors, such as, ZBTB1. Zbtb1 deletion diminishes HSC engraftment and T cell potential; by contrast, reinstating Zbtb1 in megakaryocytic-biased Kithi HSCs rescues hematopoietic engraftment and T cell potential in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, age-associated decline in Kitlo HSCs is associated with diminished T lymphopoietic potential in aged BM precursors; meanwhile, Kitlo HSCs in aged mice maintain enhanced lymphoid potential, but their per-cell capacity is diminished. Lastly, we observe an analogous human BM KITlo HSC subset with enhanced lymphoid potential. Our results thus uncover an age-related epigenetic regulation of lymphoid-competent Kitlo HSCs for T cell reconstitution.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: M.R.M.vdB. has received research support and stock options from Seres Therapeutics and stock options from Notch Therapeutics and Pluto Therapeutics; he has received royalties from Wolters Kluwer; has consulted, received honorarium from or participated in advisory boards for Seres Therapeutics, WindMIL Therapeutics, Rheos Medicines, Merck & Co, Inc., Magenta Therapeutics, Frazier Healthcare Partners, Nektar Therapeutics, Notch Therapeutics, Forty Seven Inc., Priothera, Ceramedix, Lygenesis, Pluto Therapeutics, GlaskoSmithKline, Da Volterra, Vor BioPharma, Novartis (Spouse), Synthekine (Spouse), and Beigene (Spouse); he has IP Licensing with Seres Therapeutics and Juno Therapeutics; and holds a fiduciary role on the Foundation Board of DKMS (a nonprofit organization). The Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research receives milestone and royalty payments related to venetoclax. Employees are entitled to receive benefits related to these payments. M.G.K. is a member of the scientific advisory board of 858 Therapeutics, and the laboratory gets research support from AstraZeneca and Transition Bio. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K08 HL156082/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL164902/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA023766/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA228308/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK101989-01A1/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R01 CA193842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35-CA284024/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01 CA225231/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA274249/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA186702/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA284024/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK101989/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA254838/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL135564/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG052359/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA283578/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01CA193842-01/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

