Cx43 enhances response to BRAF/MEK inhibitors by reducing DNA repair capacity
- PMID: 40615399
- PMCID: PMC12227752
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-60971-3
Cx43 enhances response to BRAF/MEK inhibitors by reducing DNA repair capacity
Abstract
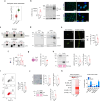
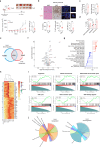
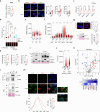
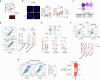
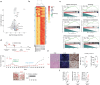
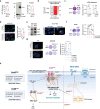
BRAF and MEK inhibitors (BRAF/MEKi) have radically changed the treatment landscape of advanced BRAF mutation-positive tumours. However, limited efficacy and emergence of drug resistance are major barriers for successful treatments. Here, by using relevant preclinical models, we find that Connexin43 (Cx43), a protein that plays a role in cell-to-cell communication, enhances the effectiveness of BRAF/MEKi by recruiting DNA repair complexes to lamin-associated domains and promoting persistent DNA damage and cellular senescence. The nuclear compartmentalization promoted by Cx43 contributes to genome instability and synthetic lethality caused by excessive DNA damage, which could provide a therapeutic approach for these tumours to overcome drug resistance. Based on these findings, we designed a drug combination using small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) to deliver the full-Cx43 in combination with the BRAF/MEKi. This study reveals Cx43 as a regulator of DNA repair and BRAF/MEKi response, highlighting the therapeutic potential that this approach could eventually have in the clinic to overcome the limitations of current therapies and improve treatment outcomes for patients with advanced BRAF mutant tumours.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

