Reconfigurable model clusters for scalable modelling of feed drive dynamics
- PMID: 40615513
- PMCID: PMC12227671
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-90325-4
Reconfigurable model clusters for scalable modelling of feed drive dynamics
Abstract
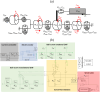
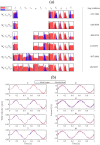
This paper presents a novel approach to modeling feed drive dynamics in machine tools. Instead of building and calibrating separate models for each machine, this approach leverages a cluster of pre-calibrated models to represent a fleet of similar machines or a single machine under varying conditions. Bayesian model selection assimilates the internal controller signals into the model cluster, selecting an optimal combination of the models to represent individual machines accurately. This approach facilitates the large-scale development of machine tool digital twins and shadows without additional modeling or experimental calibration. The effectiveness of the proposed approach is demonstrated through numerical simulations with known ground truths. The results highlight the concept's potential to simplify and scale feed drive modeling. Additionally, they outline the key technical and operational considerations necessary for its broader application.
Keywords: Bayesian model updating; Feed drives; Machine tool dynamics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The author(s) declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Development of a machine learning model and a web application for predicting neurological outcome at hospital discharge in spinal cord injury patients.Spine J. 2025 Jul;25(7):1483-1493. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2025.01.005. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Spine J. 2025. PMID: 39894282
-
An optimal neural network to design generators and stabilizers for multi-machine power systems based on a promoted firefly algorithm.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21663. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05547-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40596328 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Dataset and machine learning-based computer-aided tools for modeling working sorption isotherms in dried parchment and green coffee beans.Data Brief. 2025 May 31;61:111738. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2025.111738. eCollection 2025 Aug. Data Brief. 2025. PMID: 40612476 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altintas, Y., Verl, A., Brecher, C., Uriarte, L. & Pritschow, G. Machine tool feed drives. CIRP Ann.60, 779–796. 10.1016/j.cirp.2011.05.010 (2011).
-
- Li, C., Xu, M., Song, W. & Zhang, H. A review of static and dynamic analysis of ball screw feed drives, recirculating linear guideway, and ball screw. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf.188, 104021. 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2023.104021 (2023).
-
- Butler, Q., Ziada, Y., Stephenson, D. & Andrew Gadsden, S. Condition monitoring of machine tool feed drives: a review. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng.144, 100802 (2022).
-
- Liu, C., Vengayil, H., Zhong, R. Y. & Xu, X. A systematic development method for cyber-physical machine tools. J. Manuf. Syst.48, 13–24 (2018).
-
- Liu, C., Vengayil, H., Lu, Y. & Xu, X. A cyber-physical machine tools platform using opc ua and mtconnect. J. Manuf. Syst.51, 61–74 (2019).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

