Responsible Artificial Intelligence governance in oncology
- PMID: 40615544
- PMCID: PMC12227680
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-025-01794-w
Responsible Artificial Intelligence governance in oncology
Abstract
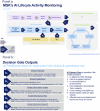
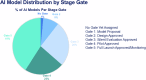
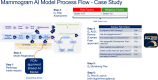
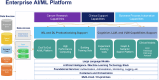
The use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in healthcare is expanding rapidly, including in oncology. Although generic AI development and implementation frameworks exist in healthcare, no effective governance models have been reported in oncology. Our study reports on a Comprehensive Cancer Center's Responsible AI governance model for clinical, operations, and research programs. We report our one-year AI Governance Committee results with respect to the registration and monitoring of 26 AI models (including large language models), 2 ambient AI pilots, and a review of 33 nomograms. Novel management tools for AI governance are shared, including an overall program model, model information sheet, risk assessment tool, and lifecycle management tool. Two AI model case studies illustrate lessons learned and our "Express Pass" methodology for select models. Open research questions are explored. To the best of our knowledge, this is one of the first published reports on Responsible AI governance at scale in oncology.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Anaeze C. Offodile, 2nd, is a board member of the Peterson Health Technology Institute. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Research status, hotspots and perspectives of artificial intelligence applied to pain management: a bibliometric and visual analysis.Updates Surg. 2025 Jun 28. doi: 10.1007/s13304-025-02296-w. Online ahead of print. Updates Surg. 2025. PMID: 40580377
-
Artificial intelligence for detecting keratoconus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Nov 15;11(11):CD014911. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014911.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37965960 Free PMC article.
-
Adoption of artificial intelligence in healthcare: survey of health system priorities, successes, and challenges.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2025 Jul 1;32(7):1093-1100. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocaf065. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2025. PMID: 40323320 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of artificial intelligence on the endoscopic assessment of inflammatory bowel disease-related neoplasia.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025 Jun 23;18:17562848251348574. doi: 10.1177/17562848251348574. eCollection 2025. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40556746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuraminidase inhibitors for preventing and treating influenza in healthy adults and children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jan 18;1:CD008965. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008965.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 10;(4):CD008965. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008965.pub4. PMID: 22258996 Updated.
Cited by
-
Incorporating large language models as clinical decision support in oncology: the Woollie model.NPJ Digit Med. 2025 Aug 18;8(1):529. doi: 10.1038/s41746-025-01941-3. NPJ Digit Med. 2025. PMID: 40825846 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Riaz, I. B., Khan, M. A. & Haddad, T. C. Potential application of artificial intelligence in cancer therapy. Curr. Opin. Oncol.36, 437–448 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Ferber, D. et al. GPT-4 for Information retrieval and comparison of Medical Oncology Guidelines. NEJM AI1, AIcs2300235 (2024).
-
- Federal Drug Administration (FDA). Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML)-Enabled Medical Devices. 2024. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/software-medical-device-samd/artific....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

