CAF-derived exosomal miR-196b-5p after androgen deprivation therapy promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer cells through HOXC8/NF-κB signaling pathway
- PMID: 40615904
- PMCID: PMC12232169
- DOI: 10.1186/s13062-025-00667-2
CAF-derived exosomal miR-196b-5p after androgen deprivation therapy promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer cells through HOXC8/NF-κB signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) have been reported to play a significant role in the development and metastasis of various tumors; however, research on their role in promoting prostate cancer (PCa) metastasis under castration conditions remains unclear.
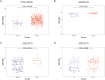
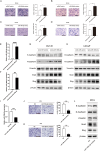
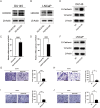
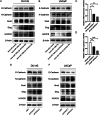
Methods: In this study, we utilized quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) to detect the expression differences of microRNA-196b-5p (miR-196b-5p) in the exosomes secreted by CAFs before and after castration. We further characterized the transcriptional regulatory landscape through RNA sequencing combined with bioinformatics databases. In vitro and in vivo experiments were conducted to determine the role of miR-196b-5p in promoting tumor migration and metastasis. The dual-luciferase reporter assay, RT-PCR analysis, and Western blot analysis confirmed that miR-196b-5p targets HOXC8 in prostate cancer. Additionally, transwell assays and Western blot analysis were performed to elucidate the role and specific mechanisms of HOXC8 in tumor metastasis.
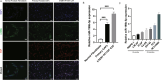
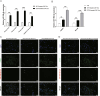
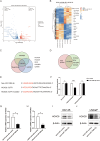
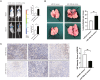
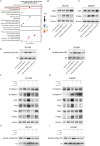
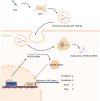
Results: By analyzing the expression differences of miRNAs in the exosomes secreted by CAFs before and after castration, along with relevant data from databases, we found that miR-196b-5p is highly secreted by CAFs after castration. miR-196b-5p promotes the migration and metastasis of prostate cancer cells. Subsequently, through RNA sequencing analysis and experimental validation, we determined that miR-196b-5p targets HOXC8. This interaction activates the NF-κB pathway, leading to the upregulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related protein expression, thereby driving the metastasis of prostate cancer.
Conclusions: Our study elucidates a specific mechanism by which CAF-derived exosomes promote prostate cancer metastasis via miR-196b-5p regulation, contributing to the identification of therapeutic targets for managing tumor metastasis following castration.
Keywords: Cancer-associated fibroblasts; Exosome; HOXC8; NF-κB; Prostate cancer; miR-196b-5p.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rab27a+CAF exosomal miR-9-5p promotes osteosarcoma progression via CREBRF/MAPK signaling pathway.Cell Signal. 2025 Oct;134:111964. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2025.111964. Epub 2025 Jun 26. Cell Signal. 2025. PMID: 40581265
-
Identification of miRNA signature in cancer-associated fibroblast to predict recurrent prostate cancer.Comput Biol Med. 2024 Sep;180:108989. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.108989. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Comput Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 39142223
-
Breast cancer-derived exosomal miR-105-5p facilitates the transformation of NFs into CAFs through LATS2-NF-κB signaling.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2025 Mar 27;57(7):1047-1056. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2025017. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2025. PMID: 40151143 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of the prognostic significance of microRNAs related to metastatic and EMT process among prostate cancer patients.J Transl Med. 2021 Jan 7;19(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02644-x. J Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33413466 Free PMC article.
-
The role of mir-151a-5p in tumorigenesis; A systematic review.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Sep;249:154576. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154576. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37562284
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global Cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49. - PubMed
-
- Gillessen S, Attard G, Beer TM, Beltran H, Bjartell A, Bossi A, Briganti A, Bristow RG, Chi KN, Clarke N et al. Management of Patients with Advanced Prostate Cancer: Report of the Advanced Prostate Cancer Consensus Conference 2019. European Urology 2020, 77(4):508–547. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Li N, Liu Q, Guo J, Pan Q, Cheng B, Xu J, Dong B, Yang G, Yang B et al. Antiandrogen treatment induces stromal cell reprogramming to promote castration resistance in prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 2023, 41(7). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

