Machine learning-based prognostic prediction for acute ischemic stroke using whole-brain and infarct multi-PLD ASL radiomics
- PMID: 40615945
- PMCID: PMC12228200
- DOI: 10.1186/s12880-025-01807-w
Machine learning-based prognostic prediction for acute ischemic stroke using whole-brain and infarct multi-PLD ASL radiomics
Abstract
Introduction: Accurate early prognostic prediction for acute ischemic stroke (AIS) is essential for guiding personalized treatment. This study aimed to assess the predictive value of radiomics features from whole-brain and infarct cerebral blood flow (CBF) images using multiple post-labeling delay arterial spin labeling (multi-PLD ASL), and to develop a prediction model incorporating clinical risk factors.
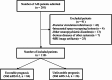
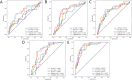
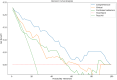
Methods: Radiomics features were extracted from the whole-brain and infarct regions based on multi-PLD ASL CBF images of 110 AIS patients. Five machine learning algorithms were used to construct radiomics models (whole-brain, infarct, and combined), clinical models, and comprehensive models integrating radiomics and clinical data. Model performance and clinical utility were assessed using receiver operating characteristic and decision curve analyses. Model stability was evaluated via 5000 permutation tests, and differences in the area under the curve (AUC) were compared using the DeLong test. Shapley Additive exPlanation was used to interpret feature contributions.
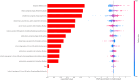
Results: The whole-brain and infarct radiomics models showed similar predictive performance. The combined radiomics models generally outperformed the infarct-only models. Additionally, no significant differences were observed between the combined radiomics models and the clinical models across the five algorithms. The comprehensive models, which integrated both radiomics and clinical features, demonstrated superior performance compared to both the clinical and combined radiomics models. Among all models, the comprehensive model based on a support vector machine achieved the highest predictive performance (AUC = 0.904). Its predictive capability was primarily driven by the baseline National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score, age, infarct shape features, and higher-order statistical and texture features derived from both infarct and whole-brain CBF images.
Conclusions: The whole-brain CBF radiomics features of multi-PLD ASL can replace the infarct radiomics features that need to be delineated. Combined radiomics models outperformed infarct-only models and performed similarly to clinical models, which is applicable to AIS patients with incomplete clinical data. The comprehensive model integrates multi-PLD ASL CBF radiomics and clinical data, providing a safe and accurate tool for early prognosis prediction in AIS patients.
Keywords: Acute ischemic stroke; Arterial spin labeling; Cerebral blood flow; Machine learning; Radiomics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was conducted according to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. Informed consent was obtained from each patient. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Yancheng Third People’s Hospital (Ethics Approval No. 2020-77). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Machine learning-based brain magnetic resonance imaging radiomics for identifying rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder in Parkinson's disease patients.BMC Med Imaging. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):227. doi: 10.1186/s12880-025-01748-4. BMC Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40597786 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of multi-PLD ASL radiomics in acute ischemic stroke.Front Neurol. 2025 Jan 13;15:1544578. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1544578. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39871992 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning-based CT radiomics enhances bladder cancer staging predictions: A comparative study of clinical, radiomics, and combined models.Med Phys. 2024 Sep;51(9):5965-5977. doi: 10.1002/mp.17288. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38977273
-
Predicting hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and methodological quality assessment of CT/MRI-based deep learning and radiomics models.Emerg Radiol. 2025 Jun;32(3):409-433. doi: 10.1007/s10140-025-02336-3. Epub 2025 Mar 26. Emerg Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40133723
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
References
-
- Pu L, Wang L, Zhang R, Zhao T, Jiang Y, Han L. Projected global trends in ischemic stroke incidence, deaths and Disability-Adjusted life years from 2020 to 2030. Stroke. 2023;54(5):1330–9. - PubMed
-
- Wu S, Wu B, Liu M, Chen Z, Wang W, Anderson CS, et al. Stroke in china: advances and challenges in epidemiology, prevention, and management. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(4):394–405. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

