Assessing the necessity of technical replicates in reverse transcription quantitative PCR
- PMID: 40616447
- PMCID: PMC12315840
- DOI: 10.1080/07366205.2025.2527536
Assessing the necessity of technical replicates in reverse transcription quantitative PCR
Abstract
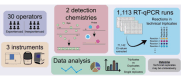
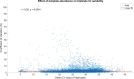
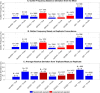
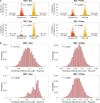
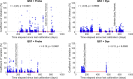
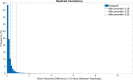
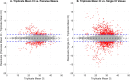
Reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) is widely used for nucleic acid quantification. The use of technical triplicates in RT-qPCR aims to minimize variability and improve reliability but increases reagent consumption, labor, and time. This study systematically evaluates the necessity of technical replicates by analyzing 71,142 cycle threshold (Ct) values from 1,113 RT-qPCR runs across three instruments, two detection chemistries, and 30 operators. Variability within replicates was assessed using metrics such as the coefficient of variation (CV), while the impacts of operator expertise, detection chemistry, instrument calibration, and initial template concentration were explored. The findings challenge the assumption that variability increases at low template concentrations, revealing no correlation between Ct values and CV. While inexperienced operators exhibited slightly higher variability, their replicates were still consistent, with acceptable CVs and low outlier frequencies. Dye-based detection showed greater variability than probe-based. Time since calibration had negligible effects on replicate consistency. Notably, duplicate or single replicates sufficiently approximated triplicate means. These results challenge traditional assumptions about RT-qPCR variability and provide a data-driven framework for optimizing experimental design. This study offers potential for resource savings without compromising data quality, particularly in high-throughput applications or laboratories with limited funds. The data underlying this article are available at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15072870.
Keywords: Assay variability; RT-qPCR; high-throughput; qPCR; reverse transcription quantitative PCR; technical replicates.
Plain language summary
We developed an automated method to assess the necessity of technical replicates in RT-qPCR by systematically analyzing cycle threshold (Ct) values obtained from multiple runs, instruments, detection chemistries, and operator groups. The approach calculates variability metrics such as the coefficient of variation and outlier frequency, and directly compares the performance of duplicate and single replicates against standard triplicates.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending, or royalties.
No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Laboratory-based molecular test alternatives to RT-PCR for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Oct 14;10(10):CD015618. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015618. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39400904
-
The effect of sample site and collection procedure on identification of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Dec 16;12(12):CD014780. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014780. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39679851 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
References
-
- Taylor S, Wakem M, Dijkman G, et al. A practical approach to RT-qPCR—publishing data that conform to the MIQE guidelines. Methods. 2010;50(4):S1–S5. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2010.01.005 - DOI - PubMed
-
• Illustrates how everyday laboratory workflows implement the MIQE guidelines, highlighting common reliance on technical triplicates.
-
- Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, et al. The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem. 2009;55(4):611–622. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2008.112797 - DOI - PubMed
-
•• Foundational guidelines that set the quality standard for qPCR reporting; it underpins the entire debate about when replicates are needed.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
