Functional characterization of genetic variants affecting the intracellular domains of ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1)
- PMID: 40617357
- PMCID: PMC12341595
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jlr.2025.100854
Functional characterization of genetic variants affecting the intracellular domains of ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1)
Abstract
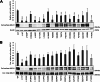
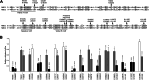
The ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) effluxes cellular cholesterol and phospholipids to extracellular acceptors, mainly apolipoprotein A1, generating high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles. This is the first step in the anti-atherosclerotic process of transporting excess cholesterol from non-hepatic tissues to the liver. Loss-of-function variants in ABCA1 lead to reduced HDL cholesterol levels in plasma, thus possibly diminishing the atheroprotective effect of HDL. More than 250 missense variants have been reported in the ABCA1 gene, most of which remain to be functionally characterized. In this study, we have characterized 74 variants affecting the intracellular domains of ABCA1 by assessing cholesterol efflux activity and cell surface localization of the protein, thereby shifting the pathogenicity classification of 10 variants from class 3 (uncertain significance) to class 4 (likely pathogenic) or class 2 (likely benign). Consequently, functional characterization contributes to a better understanding of the molecular basis of the pathogenicity of genetic variants in ABCA1, which could also clarify the mechanism of action of the protein.
Keywords: HDL; HEK293 cells; Tangier disease; cholesterol efflux; lipid metabolism; lipoproteins.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures



References
-
- WHO . World Health Organization (WHO); Geneva, Switzerland: 2021. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs)
-
- Brooks-Wilson A., Marcil M., Clee S.M., Zhang L.-H., Roomp K., van Dam M., et al. Mutations in ABC1 in Tangier disease and familial high-density lipoprotein deficiency. Nat. Genet. 1999;22:336–345. - PubMed
-
- Rust S., Rosier M., Funke H., Real J., Amoura Z., Piette J.-C., et al. Tangier disease is caused by mutations in the gene encoding ATP-binding cassette transporter 1. Nat. Genet. 1999;22:352–355. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

