Minimally invasive approach versus open approach in the management of necrotizing acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40619162
- PMCID: PMC12377997
- DOI: 10.14701/ahbps.25-068
Minimally invasive approach versus open approach in the management of necrotizing acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
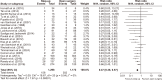
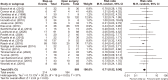
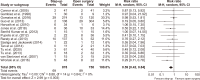
Acute pancreatitis is one of the most common gastrointestinal diseases, with necrotizing pancreatitis affecting 10% to 15% of patients. Over recent years, the management of pancreatic necrosis has evolved significantly, with a growing shift towards minimally invasive approaches. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of minimally invasive approach compared to open surgical approach in managing necrotizing acute pancreatitis. A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted, including 22 studies. Both fixed-effect and random-effect models were applied to analyze nine outcomes evaluated. Homogeneity among studies was assessed using χ2 tests, I2 statistics, and p-values. The risk of postoperative mortality, intra-abdominal bleeding, pancreatic and enteric fistulas, perforation, new-onset diabetes, and postoperative sepsis was significantly lower in the minimally invasive approach group than in the open surgical approach group. A minimally invasive approach to necrotizing acute pancreatitis might be associated with a lower risk of complications compared to an open surgical approach. However, most of the included studies were observational studies. Additional randomized trials are needed to further confirm these findings.
Keywords: Acute pancreatitis; Minimally invasive approach; Necrosis pancreatic; Open approach.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
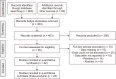




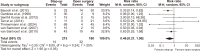
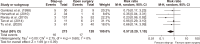

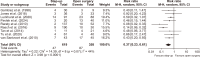
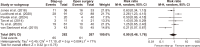
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
