Accidental dexmedetomidine overdose in preterm newborns: a report of 3 cases
- PMID: 40619398
- PMCID: PMC12232678
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-025-02060-1
Accidental dexmedetomidine overdose in preterm newborns: a report of 3 cases
Abstract
Background: Dexmedetomidine use in neonatal units is increasing. Data on its safety are still limited. There are no previous reports of clinical presentation of dexmedetomidine overdose in newborns.
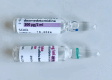
Case presentation: Three babies simultaneously developed a similar clinical picture of recurrent apneas, a typical "gasping" breathing pattern, irritability followed by hypotonia and hyporeactivity, hyperglycaemia, hypocapnia, increase in lactates and a suppression-burst pattern on CFM/EEG. Babies required intubation and mechanical ventilation due to poor respiratory effort. Symptoms resolved completely in a few hours. Dexmedetomidine was administered enterally by a nasogastric tube in place of caffeine due to "look alike" medication error. Dexmedetomidine was retrieved in biological samples. Babies were developing regularly at post-discharge follow up visits.
Conclusion: Dexmedetomidine overdose due to medication error is possible in newborns and should be suspected in case of clinical presentations similar to the one we reported. Measures should be implemented in neonatal units for a safe use of dexmedetomidine.
Keywords: Case report; Dexmedetomidine; Medication error; Newborn; Overdose.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Parents provided written informed consent; approval by Ethics committee was waived. Consent for publication: Parents provided written informed consent for publication. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Portelli K, Kandraju H, Ryu M, Shah PS. Efficacy and safety of Dexmedetomidine for analgesia and sedation in neonates: a systematic review. J Perinatol. 2024;44(2):164–72. 10.1038/s41372-023-01802-5. - PubMed
-
- Chrysostomou C, Schulman SR, Herrera Castellanos M, Cofer BE, Mitra S, da Rocha MG, Wisemandle WA, Gramlich L. A phase II/III, multicenter, safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetic study of dexmedetomidine in preterm and term neonates. J Pediatr. 2014;164(2):276– 82.e1-3. 10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.10.002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

