Novel sponge formulation of mesenchymal stem cell secretome and hyaluronic acid: a safe and effective topical therapy for Psoriasis vulgaris
- PMID: 40619420
- PMCID: PMC12232821
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-025-04415-1
Novel sponge formulation of mesenchymal stem cell secretome and hyaluronic acid: a safe and effective topical therapy for Psoriasis vulgaris
Abstract
Background: Psoriasis vulgaris is the most common form of psoriasis, yet current treatments often lead to significant side effects, resulting in a high rate of therapy desertion. Here, we explored a novel therapeutic approach using the secretome from Wharton Jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells, biologically stabilized and enhanced with hyaluronic acid (HA), its presentation is an easy-to-apply topical sponge. This formulation had previously demonstrated efficacy in vitro and in experimental psoriasis mouse models.
Methods: In vitro characterization studies included dynamic light scattering, nanoparticle tracking analysis, optical/electronic microscopy, microbiological experiments, and angiogenic capacity (HUVEC cells). In vivo studies included angiogenic capacity in chicken embryo chorioallantoic membrane (CAM), safety (hypersensitive and healthy volunteers), and efficacy (double-blinded and randomized patients).
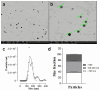
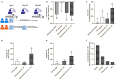
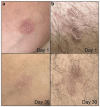
Results: We demonstrated the presence of spherical exosomes (164 ± 87 nm, PDI of 0.38, and 1.5 × 10⁷ particles/mL) within the selected secretomes, which exhibited significant proangiogenic activity in HUVEC cells and in a CAM assay. The secretome-containing sponges displayed distinct physicochemical properties, such as the absence of nitrogen and reduced carbon and oxygen content, resulting in a more cross-linked material with thinner fibers. These characteristics extended the dispersion time in aqueous media. Microbiological testing confirmed sterility in the packed, ready-to-use secretome-HA sponges after 3 months of storage. To assess safety, we selected doses (based on total protein content) that were applied to three patients with atopic dermatitis (42 µg of protein, patch test, 5 days) and four healthy volunteers (210 µg, 15 days) with no observed adverse topical or systemic effects. In a 30-day efficacy study, 12 patients with bilateral psoriasis exhibited up to a 33% reduction in mPASI scores and a 41% decrease in plaque size. Additionally, transepidermal water loss (TEWL) was reduced by up to 30%, while skin elasticity/flexibility improved by 43%.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that the topical application of the secretome-HA sponge is a safe and effective therapeutic option for alleviating symptoms of psoriasis vulgaris.
Trial registration: SSMN, SSMN047/2021. Registered 27 October 2021, https://www.ssmn.cl/comite_etica.php .
Keywords: Exosomes, hyaluronic acid, Psoriasis vulgaris; MSC-based therapy, cutometer; Mesenchymal stem cell; Secretome.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: The authors declare that they have not used AI-generated work in this manuscript. Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in this publication.
Figures



References
-
- Jafarzadeh A, Pour Mohammad A, Keramati H, Zeinali R, Khosravi M, Goodarzi A. Regenerative medicine in the treatment of specific dermatologic disorders: a systematic review of randomized controlled clinical trials. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024;15(1):176. 10.1186/s13287-024-03800-6. PMID: 38886861; PMCID: PMC11184747. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Armstrong AW, Read C, Pathophysiology. Clinical presentation, and treatment of psoriasis: A review. JAMA. 2020;323(19):1945–60. - PubMed
-
- Griffiths CE, Barker JN. Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. Lancet. 2007;370(9583):263–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

