Systematic literature review to identify prognostic factors of efficacy and safety outcomes of chimeric antigen receptor T-Cell therapies in diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma
- PMID: 40619472
- PMCID: PMC12229961
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-025-06249-z
Systematic literature review to identify prognostic factors of efficacy and safety outcomes of chimeric antigen receptor T-Cell therapies in diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma
Abstract
Purpose: To identify and summarize clinical factors influencing the efficacy and safety outcomes of CAR-T cell therapies in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) through a systematic literature review.
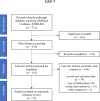
Methods: We performed a systematic literature review to identify factors impacting the efficacy and safety of CAR-T therapies in DLBCL. Articles were searched in PubMed, Cochrane, and EMBASE databases. Key outcomes, including progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), complete response rate (CRR), objective response rate (ORR), duration of response (DoR), best overall response (BOR), and safety measures (e.g., Immune Effector Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome [ICANS], and Cytokine Release Syndrome [CRS]), were extracted according to PRISMA guidelines. A total of 712 articles were identified, with 185 selected for full-text screening. Ultimately, 79 articles met inclusion criteria. Exclusions were primarily due to the absence of relevant outcome data or publication type.
Results: This review highlights several factors that may influence the efficacy and safety of CAR-T therapies in DLBCL, including Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status (ECOG PS), International Prognostic Index (IPI) score, disease histology, Ann Arbor disease stage, and elevated LDH levels.
Conclusion: The findings of this review can assist clinicians in refining treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes in DLBCL by incorporating these key influencing factors.
Keywords: CAR-T; DLBCL; Prognostic factors; Systematic literature review.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: JM, UR and SR were employees of Miltenyi Biomedicine GmbH during the conduct of the study. All authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any other organization or entity with a financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Abramson JS, Palomba ML, Gordon LI, Lunning MA, Wang M, Arnason J, Mehta A, Purev E, Maloney DG, Andreadis C, Sehgal A, Solomon SR, Ghosh N, Albertson TM, Garcia J, Kostic A, Mallaney M, Ogasawara K, Newhall K, Kim Y, Li D, Siddiqi T (2020) Lisocabtagene maraleucel for patients with relapsed or refractory large B-Cell lymphomas (Transcend Nhl 001): a multicentre seamless design study. Lancet 396:839–852 - PubMed
-
- Awasthi R, Pacaud L, Waldron E, Tam CS, Jäger U, Borchmann P, Jaglowski S, Foley SR, Van Besien K, Wagner-Johnston ND, Kersten MJ, Schuster SJ, Salles G, Maziarz RT, Anak Ö, Del Corral C, Chu J, Gershgorin I, Pruteanu-Malinici I, Chakraborty A, Mueller KT, Waller EK (2020) Tisagenlecleucel cellular kinetics, dose, and immunogenicity in relation to clinical factors in relapsed/refractory DLBCL. Blood Adv 4(3):560–572 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ayuk FA, Berger C, Badbaran A, Zabelina T, Sonntag T, Riecken K, Geffken M, Wichmann D, Frenzel C, Thayssen G, Zeschke S, Kröger N, Fehse B (2021) Axicabtagene ciloleucel in vivo expansion and treatment outcome in aggressive B-Cell lymphoma in a real-world setting. Blood Adv 5(11):2523–2527 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bachy E, Le Gouill S, Di Blasi R, Sesques P, Manson G, Cartron G, Beauvais D, Roulin L, Gros FX, Rubio MT, Bories P, Bay JO, Llorente CC, Choquet S, Casasnovas RO, Mohty M, Guidez S, Joris M, Loschi M, Carras S, Abraham J, Chauchet A, Drieu La Rochelle L, Deau-Fischer B, Hermine O, Gastinne T, Tudesq JJ, Gat E, Broussais F, Thieblemont C, Houot R, Morschhauser F (2022) A real-world comparison of tisagenlecleucel and axicabtagene ciloleucel CAR T cells in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Nat Med 28:2145–2154 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous