Advanced Nanomedicines for Treating Refractory Inflammation-Related Diseases
- PMID: 40619552
- PMCID: PMC12229986
- DOI: 10.1007/s40820-025-01829-7
Advanced Nanomedicines for Treating Refractory Inflammation-Related Diseases
Abstract
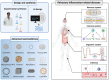
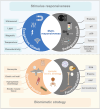
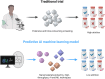
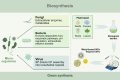
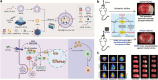
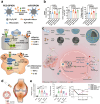
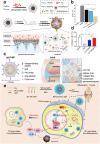
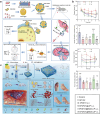
This review examines inflammation as a physiological defense mechanism against infectious agents, physical trauma, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and metabolic stress, which, under dysregulated conditions, may progress into chronic diseases. Nanomedicine, which integrates nanotechnology with medicine, suppresses inflammatory signaling pathways and overexpressed pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as ROS, to address inflammation-related pathologies. Current advances in nanomaterial design and synthesis strategies are systematically analyzed, with parallel discussions on toxicity mechanisms, influencing factors, and evaluation methods that are critical for clinical translation. Applications of functional nanomaterials are highlighted in the context of refractory inflammatory conditions, including wound healing, gastrointestinal disorders, and immune, neurological, or circulatory diseases, along with targeted delivery strategies. Persistent challenges in nanomedicine development, such as biocompatibility optimization, precise biodistribution control, and standardized toxicity assessment, are critically assessed. By bridging material innovation with therapeutic efficacy, this review establishes a framework for advancing nanomedicine to improve treatment outcomes while addressing translational barriers.
Keywords: Nanomedicine; Nanoparticles; Nanozymes; Pancatalysis; ROS scavenging.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no interest conflict. They have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome.2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31613449 Free Books & Documents.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
[Guidelines for the prevention and management of bronchial asthma (2024 edition)].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2025 Mar 12;48(3):208-248. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112147-20241013-00601. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40050074 Chinese.
References
-
- P.D. Kilmer, Nanomedicine. N. Engl. J. Med. 363, 2434–2443 (2010). 10.1177/1461444810365020
-
- C. Zhang, L. Yan, X. Wang, S. Zhu, C. Chen et al., Progress, challenges, and future of nanomedicine. Nano Today 35, 101008 (2020). 10.1016/j.nantod.2020.101008
-
- D. Nie, C. Liu, M. Yu, X. Jiang, N. Wang et al., Elasticity regulates nanomaterial transport as delivery vehicles: design, characterization, mechanisms and state of the art. Biomaterials 291, 121879 (2022). 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121879 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
