Generative Artificial Intelligence in Prostate Cancer Imaging
- PMID: 40619793
- PMCID: PMC12240228
- DOI: 10.4274/balkanmedj.galenos.2025.2025-4-69
Generative Artificial Intelligence in Prostate Cancer Imaging
Abstract
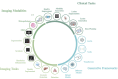
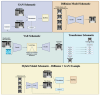
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the second most common cancer in men and has a significant health and social burden, necessitating advances in early detection, prognosis, and treatment strategies. Improvement in medical imaging has significantly impacted early PCa detection, characterization, and treatment planning. However, with an increasing number of patients with PCa and comparatively fewer PCa imaging experts, interpreting large numbers of imaging data is burdensome, time-consuming, and prone to variability among experts. With the revolutionary advances of artificial intelligence (AI) in medical imaging, image interpretation tasks are becoming easier and exhibit the potential to reduce the workload on physicians. Generative AI (GenAI) is a recently popular sub-domain of AI that creates new data instances, often to resemble patterns and characteristics of the real data. This new field of AI has shown significant potential for generating synthetic medical images with diverse and clinically relevant information. In this narrative review, we discuss the basic concepts of GenAI and cover the recent application of GenAI in the PCa imaging domain. This review will help the readers understand where the PCa research community stands in terms of various medical image applications like generating multi-modal synthetic images, image quality improvement, PCa detection, classification, and digital pathology image generation. We also address the current safety concerns, limitations, and challenges of GenAI for technical and clinical adaptation, as well as the limitations of current literature, potential solutions, and future directions with GenAI for the PCa community.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Using Generative Artificial Intelligence in Health Economics and Outcomes Research: A Primer on Techniques and Breakthroughs.Pharmacoecon Open. 2025 Jul;9(4):501-517. doi: 10.1007/s41669-025-00580-4. Epub 2025 Apr 29. Pharmacoecon Open. 2025. PMID: 40301283 Free PMC article.
-
MRI software and cognitive fusion biopsies in people with suspected prostate cancer: a systematic review, network meta-analysis and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(61):1-310. doi: 10.3310/PLFG4210. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367754 Free PMC article.
-
Generative Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Medicine and Impact on Gastroenterology.Gastroenterology. 2025 Aug;169(3):502-517.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.03.038. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Gastroenterology. 2025. PMID: 40245953 Review.
-
Generative Artificial Intelligence in Nuclear Medicine Education.J Nucl Med Technol. 2025 Mar 5;53(1):72-79. doi: 10.2967/jnmt.124.268323. J Nucl Med Technol. 2025. PMID: 39909578 Review.
-
The impact of artificial intelligence on the endoscopic assessment of inflammatory bowel disease-related neoplasia.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025 Jun 23;18:17562848251348574. doi: 10.1177/17562848251348574. eCollection 2025. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40556746 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2025. In: The American Cancer Society Medical and Editorial Content Team, editor. Atlanta:American Cancer Society.2025.
-
- Gravestock P, Shaw M, Veeratterapillay R, Heer R. Prostate cancer diagnosis: biopsy approaches. In: Barber N, Ali A, editors. Urologic Cancers. Brisbane (AU).2022. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
