Discovery of conformation constrained tetracyclic compounds as potent chitinase Of Chi-h inhibitors with a novel binding mode
- PMID: 40619956
- PMCID: PMC12239106
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2025.2528056
Discovery of conformation constrained tetracyclic compounds as potent chitinase Of Chi-h inhibitors with a novel binding mode
Abstract
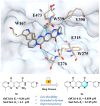
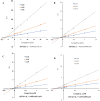
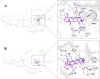
Chitinase h (Chi-h) has been identified as a promising pesticide target due to its exclusive distribution in lepidopteran insects and its essential role in the moulting processes. In this study, we leverage OfChi-h from destructive agricultural pest Ostrinia furnacalis (Asian corn borer) as a model target to identify novel chitinase inhibitors. A conformational restriction approach was employed to design a series of novel OfChi-h inhibitors. Among these, compound 6a showed the highest inhibitory activity against OfChi-h, with a Ki value of 58 nM. Molecular docking analysis suggested that 6a tightly bound to three subsites (-3 to -1) of OfChi-h. The binding mode is further confirmed by the co-crystallization data of 6a with the SmChiA, a bacterial homologue of OfChi-h, at a resolution of 1.8 Å. This research presents a novel approach for the development of highly potent insect chitinase inhibitors, offering potential tools for effective pest control.
Keywords: Chitinase; conformation restriction; inhibitor; inhibitory mechanism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors claim no conflict of interest about this work.
Figures
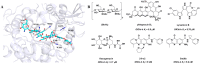



Similar articles
-
Discovery of Azo-Aminopyrimidines as Novel and Potent Chitinase OfChi-h Inhibitors via Structure-Based Virtual Screening and Rational Lead Optimization.J Agric Food Chem. 2022 Sep 28;70(38):12203-12210. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c03997. Epub 2022 Sep 19. J Agric Food Chem. 2022. PMID: 36121180
-
Rational design of azo-aminopyrimidine derivatives as the potent lepidoptera-exclusive chitinase inhibitors.Plant Biotechnol J. 2025 Mar;23(3):780-791. doi: 10.1111/pbi.14538. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Plant Biotechnol J. 2025. PMID: 39666783 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, Catalysis, and Inhibition of OfChi-h, the Lepidoptera-exclusive Insect Chitinase.J Biol Chem. 2017 Feb 10;292(6):2080-2088. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.755330. Epub 2017 Jan 4. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28053084 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Chen W, Yang Q.. Development of novel pesticides targeting insect chitinases: a minireview and perspective. J Agric Food Chem. 2020;68(16):4559–4565. - PubMed
-
- Lu Q, Xie H, Qu M, Liu T, Yang Q.. Group h chitinase: a molecular target for the development of lepidopteran-specific insecticides. J Agric Food Chem. 2023;71(15):5944–5952. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Jiang X, Yang Q.. Glycoside hydrolase family 18 chitinases: the known and the unknown. Biotechnol Adv. 2020;43:107553. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
