Small and Large Extracellular Vesicles From Human Preovulatory Follicular Fluid Display Distinct ncRNA Cargo Profiles and Differential Effects on KGN Granulosa Cells
- PMID: 40620085
- PMCID: PMC12230353
- DOI: 10.1002/jev2.70119
Small and Large Extracellular Vesicles From Human Preovulatory Follicular Fluid Display Distinct ncRNA Cargo Profiles and Differential Effects on KGN Granulosa Cells
Abstract
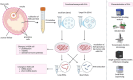
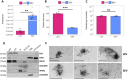
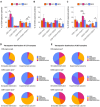
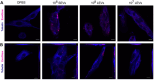
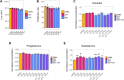
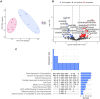
Follicular fluid extracellular vesicles (FF EVs) facilitate communication between oocytes and somatic cells within the ovarian follicle, playing a pivotal role in follicular development. This study highlights the molecular and functional distinctions between small (SEV) and large (LEV) FF EV subpopulations, revealing their specialised regulatory roles in granulosa cell (GC) biology and their consequential impact on ovarian function. Single-EV profiling uncovered distinct tetraspanin distributions, with LEVs containing a lower proportion of CD9/CD63/CD81-positive particles compared to SEVs. Fluorescent labelling confirmed uptake of both SEVs and LEVs by GCs, supporting their capacity to impact cellular behaviour. Functionally, LEVs increased testosterone production by GCs, whilst SEVs had no effect on steroid hormone secretion, suggesting a specific role for LEVs in androgen biosynthesis. Transcriptomic analysis revealed extensive SEV-induced changes in GC gene expression, affecting pathways involved in transcription, TGF-β signalling, extracellular matrix (ECM) remodelling and cell cycle regulation. In contrast, LEVs elicited minimal transcriptional changes, primarily modulating genes associated with immune regulation and oxidative stress defence. Small RNA sequencing further revealed distinct non-coding RNA (ncRNA) profiles, with SEVs enriched in miRNAs targeting pathways critical for GC differentiation, whilst LEVs carried higher levels of piRNAs implicated in maintaining genomic stability. These findings advance our understanding of FF EV-mediated intercellular communication and underscore the importance of investigating EV subpopulations independently.
Keywords: extracellular vesicles; follicular fluid; granulosa cells; miRNA; ncRNA; ovary.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Extracellular Vesicles published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
Paolo Guazzi is the Chief Operating Officer at HansaBioMed Life Sciences. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Follicular-fluid extracellular vesicles support energy metabolism of bovine oocytes, improving blastocyst development and quality†.Biol Reprod. 2025 Jul 13;113(1):109-126. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioaf096. Biol Reprod. 2025. PMID: 40272384 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and characterization of bone mesenchymal cell small extracellular vesicles using a novel mouse model.J Bone Miner Res. 2024 Oct 29;39(11):1633-1643. doi: 10.1093/jbmr/zjae135. J Bone Miner Res. 2024. PMID: 39173022
-
Single vesicle analysis reveals the release of tetraspanin positive extracellular vesicles into circulation with high intensity intermittent exercise.J Physiol. 2023 Nov;601(22):5093-5106. doi: 10.1113/JP284047. Epub 2023 Mar 16. J Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36855276 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming challenges in MSC-sEV therapeutics: insights and advances after a decade of research.Cytotherapy. 2025 Jul;27(7):843-848. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2025.03.505. Epub 2025 Mar 20. Cytotherapy. 2025. PMID: 40243980 Review.
-
Harnessing EVs-ncRNA for Lung Cancer: From Oncogenic Pathways to Novel Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jul 14;20:9031-9054. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S528115. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40689018 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andrews, S. 2010. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data . Available online at: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

