Chinese Expert Consensus on Standardized Outpatient Management of Sarcopenia in the Elderly (2024)
- PMID: 40620514
- PMCID: PMC12226417
- DOI: 10.1002/agm2.70010
Chinese Expert Consensus on Standardized Outpatient Management of Sarcopenia in the Elderly (2024)
Abstract
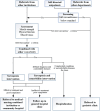
Sarcopenia is an age-related disorder that influences the daily living ability of older adults and interacts with various chronic diseases. Older adults with sarcopenia typically experience a deterioration in their quality of life and healthy lifespan. The number of Chinese persons with sarcopenia is considerable, and the burden of sarcopenia is substantial; however, the specific sarcopenia clinics available for outpatients are insufficient. The promotion of sarcopenia clinics is beneficial for the early identification, standardized diagnosis, and treatment of older adults with sarcopenia, thereby helping to enhance their physical function and quality of life. This consensus incorporates the professional recommendations of Chinese geriatrics experts, synthesizes existing Chinese experiences in establishing sarcopenia clinics, offers guidance for managing sarcopenia clinics, and advocates for early identification, diagnosis, and intervention of sarcopenia in older adults.
Keywords: clinic management; expert consensus; older adults; sarcopenia.
© 2025 The Author(s). Aging Medicine published by Beijing Hospital and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Wang Jianye, Yu Pulin, Kang Lin, Zhang Qin, and Zhang Cuntai are the Editorial Board members of the journal and were excluded from the peer‐review process and all editorial decisions related to the publication of this article. Other authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Liu J., Ding Q. Q., Zhou B. Y., et al., “Chinese Expert Consensus on Diagnosis and Treatment for Elderly With Sarcopenia,” Chinese Journal of Geriatric 40, no. 8 (2021): 943–952, 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-9026.2021.08.001. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources