Potential of miR-192-5p as a diagnostic marker for children with severe pneumonia and respiratory failure and its predictive value for prognosis
- PMID: 40620650
- PMCID: PMC12224244
- DOI: 10.5114/ceji.2025.149249
Potential of miR-192-5p as a diagnostic marker for children with severe pneumonia and respiratory failure and its predictive value for prognosis
Abstract
Introduction: Severe pneumonia in children is a rapidly progressing respiratory system disease. If not promptly controlled, it can lead to respiratory failure, posing a serious threat to the child's life. This study investigated the diagnostic and prognostic potential of miR-192-5p in children with severe pneumonia and respiratory failure.
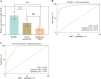
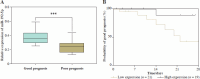
Material and methods: A total of 62 children with severe pneumonia, 40 children with severe pneumonia and respiratory failure, and 62 healthy children were enrolled. The level of miR-192-5p was quantified by RT-qPCR assays. The diagnostic potential of miR-192-5p for severe pneumonia and respiratory failure was assessed through ROC curve and binary logistic analyses. The association between abnormal miR-192-5p level and prognosis of children with severe pneumonia with respiratory failure was evaluated by Kaplan-Meier and multivariate Cox analysis.
Results: miR-192-5p expression was decreased in the serum of severe pneumonia and expiratory failure children. miR-192-5p has a good potential to predict the occurrence of severe pneumonia, which is a risk predictor of severe pneumonia in children with respiratory failure. In addition, downregulation of miR-192-5p was strongly associated with poor prognosis of children with severe pneumonia and respiratory failure.
Conclusions: A low level of miR-192-5p has high predictive value and clinical development potential for the timely diagnosis and prediction of poor prognosis of children with severe pneumonia and respiratory failure.
Keywords: diagnosis; miR-192-5p; prognosis; respiratory failure; severe pneumonia.
Copyright © 2025 Termedia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
miR-486-5p predicted adverse outcomes of SCAP and regulated K. pneumonia infection via FOXO1.BMC Immunol. 2024 Jun 4;25(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12865-024-00624-0. BMC Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38834979 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of serum miR-98-5p in children with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection complicated with digestive system damage.Immunobiology. 2025 Jul;230(4):153101. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2025.153101. Epub 2025 Jul 15. Immunobiology. 2025. PMID: 40712324
-
Diagnostic Value of Serum miR-499a-5p in Chinese Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders.J Mol Neurosci. 2025 Jan 21;75(1):8. doi: 10.1007/s12031-024-02296-2. J Mol Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39836335
-
Systematic review and validation of prediction rules for identifying children with serious infections in emergency departments and urgent-access primary care.Health Technol Assess. 2012;16(15):1-100. doi: 10.3310/hta16150. Health Technol Assess. 2012. PMID: 22452986 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yanase F, Naorungroj T, Bellomo RJB (2020): Glycocalyx damage biomarkers in healthy controls, abdominal surgery, and abdominal surgery sepsis: a scoping review. Biomarkers 25: 425-435. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
