Quantifying social distance using deep learning-based video analysis: results from the BTBR mouse model of autism
- PMID: 40620906
- PMCID: PMC12226490
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2025.1602205
Quantifying social distance using deep learning-based video analysis: results from the BTBR mouse model of autism
Abstract
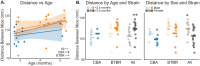
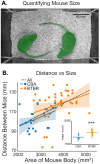
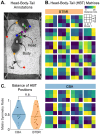
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is characterized by challenges in social communication, difficulties in understanding social cues, a tendency to perform repetitive behaviors, and restricted interests. BTBR T+ Itpr3tf/J (BTBR) mice exhibit ASD-like behavior and are often used to study the biological basis of ASD. Social behavior in BTBR mice is typically scored manually by experimenters, which limits the precision and accuracy of behavioral quantification. Recent advancements in deep learning-based tools for machine vision, such as DeepLabCut (DLC), enable automated tracking of individual mice housed in social groups. Here, we used DLC to measure locomotion and social distance in pairs of familiar mice. We quantified social distance by finding the Euclidean distance between pairs of tracked mice. BTBR mice showed hyperlocomotion and greater social distance than CBA control mice. BTBR social distance was consistently greater than CBA control mice across the duration of a 60-min experiment. Despite exhibiting greater social distance, BTBR mice showed comparable socio-spatial arrangements of heads, bodies, and tails compared to CBA control mice. We also found that age, sex, and body size may affect social distance. Our findings demonstrate that DeepLabCut facilitates the quantification of social distance in BTBR mice, providing a complementary tool for existing behavioral assays.
Keywords: BTBR; CBA; DeepLabCut; autism; mice; social distance.
Copyright © 2025 Khan, Cherkas and Francis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
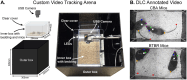
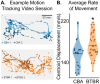
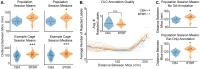
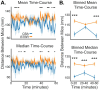
References
-
- Avolio E., Olivito I., Leo A., De Matteo C., Guarnieri L., Bosco F., et al. (2024). Vasostatin-1 restores autistic disorders in an idiopathic autism model (BTBR T+ Itpr3(tf)/J mice) by decreasing hippocampal neuroinflammation. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 135:111131. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2024.111131, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

