Antiproliferative and Trypanocidal Activity of Ivermectin Bioconjugates
- PMID: 40621026
- PMCID: PMC12223813
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c02998
Antiproliferative and Trypanocidal Activity of Ivermectin Bioconjugates
Abstract
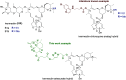
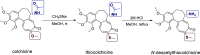
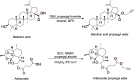
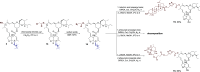
Ivermectin (IVR), whose discovery has been Nobel-Prize-honored, is a 16-membered macrocyclic lactone used in medicine as an extremely effective and safe antiparasitic drug. In recent years, interest in this compound has grown due to its potential effectiveness in killing various types of cancer cells. However, research on the anticancer activity of IVR derivatives is limited. Additionally, the growing problem of drug resistance raises concerns about the effectiveness of this drug in the treatment of parasitic diseases. Therefore, in this work, we provide a detailed description of the synthesis of ten new IVR bioconjugates with compounds exhibiting high anticancer and/or antimicrobial activity. We also assess the effectiveness of these hybrids in killing Trypanosoma brucei brucei a protozoan parasite that causes African trypanosomiasis, as well as their anticancer activity toward various cancer cell lines. Many of the newly synthesized conjugates exhibited higher biological activity than their respective parent compounds as well as increased selectivity indices. The IVR conjugate with artesunate (compound 16) appears particularly interesting, as it proved not only to be several times more active than the parent compounds but also showed no toxicity toward a reference cell line, indicating its potential as a therapeutic agent.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization . Cancer, https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer. (on-line access: 2025–04–02)
-
- Global Cancer Observatory , https://gco.iarc.fr/. (on-line access: 2025–04–02).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
