Interaction of Anionic Surfactants with Native and Partially Unfolded RNase A: Binding Kinetics, Structural Changes, and Stability
- PMID: 40621027
- PMCID: PMC12223854
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c01998
Interaction of Anionic Surfactants with Native and Partially Unfolded RNase A: Binding Kinetics, Structural Changes, and Stability
Abstract
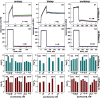
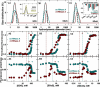
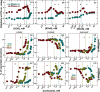
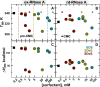
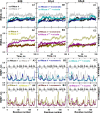
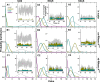
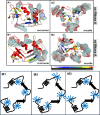
In protein-surfactant interactions, the alkyl chain length of surfactants and the surface-exposed residues of proteins play essential roles in binding and unfolding. To investigate this, the interactions of sodium octyl (SOS), decyl (SDeS), and dodecyl (SDoS) sulfates were studied with native and partially unfolded forms of ribonuclease A (ox-RNase A and rd-RNase A) by using surface plasmon resonance (SPR), optical spectroscopy, and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. rd-RNase A was obtained by partial reduction of the disulfide bonds of RNase A. MD simulations of RNase A in its native and unfolded states were carried out in the presence of all three surfactants in their monomeric and micellar concentrations, respectively. The binding affinity of surfactants differs between ox-RNase A and rd-RNase A. Monomeric forms of the surfactants do not affect the structure and stability of either form of RNase A. Upon micelle formation of the surfactants, ox-RNase A loses its tertiary interactions along with β-sheets. However, it forms non-native α-helices that gradually destabilize ox-RNase A. rd-RNase A initially forms more β-sheets, which stabilize the protein. Further increases in surfactant concentrations destabilize the β-sheets and induce the formation of non-native α-helices. MD simulation results suggest that rd-RNase A induces micelle formation with higher aggregation numbers than ox-RNase A. At monomeric concentrations, the interactions of surfactants could be predominantly ionic, whereas at micellar concentrations, hydrophobic interactions contribute significantly. The exposed hydrophobic surfaces of partially unfolded rd-RNase A facilitate binding of the surfactant to the protein. This results in differences in the unfolding pathways of rd-RNase A and ox-RNase A.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures


References
-
- Kralova I., Sjöblom J.. Surfactants Used in Food Industry: A Review. J. Dispers Sci. Technol. 2009;30(9):1363–1383. doi: 10.1080/01932690902735561. - DOI
-
- Shaban S. M., Kang J., Kim D.-H.. Surfactants: Recent Advances and Their Applications. Composites Communications. 2020;22:100537. doi: 10.1016/j.coco.2020.100537. - DOI
-
- Moon S. Y., Kusunose T., Sekino T.. CTAB-Assisted Synthesis of Size- and Shape-Controlled Gold Nanoparticles in SDS Aqueous Solution. Mater. Lett. 2009;63:2038–2040. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2009.06.047. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
