Evaluation of a novel aspergillus IgG lateral flow assay for the diagnosis of non-neutropenic patients with acute and subacute invasive aspergillosis
- PMID: 40621162
- PMCID: PMC12226544
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1599425
Evaluation of a novel aspergillus IgG lateral flow assay for the diagnosis of non-neutropenic patients with acute and subacute invasive aspergillosis
Erratum in
-
Correction: Evaluation of a novel Aspergillus IgG lateral flow assay for the diagnosis of non-neutropenic patients with acute and subacute invasive aspergillosis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jul 25;15:1659574. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1659574. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40786609 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to assess a novel lateral flow assay (LFA) for Aspergillus IgG detection in patients with non-neutropenic invasive aspergillosis (IA).
Methods: Aspergillus IgG LFA and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) were performed in non-neutropenic IA patients and control group (proven community acquired pneumonia and healthy persons), respectively. The diagnostic performance of Aspergillus IgG LFA for IA was evaluated and compared with ELISA method.
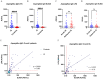
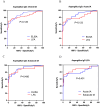
Results: 33 cases of acute IA, 30 cases of subacute IA and 80 controls were enrolled in this study. The level of plasma Aspergillus IgG LFA in the IA group was significantly higher than that in the control group (190.5 AU/mL vs. 50.3 AU/mL, P < 0.001). In total, the sensitivity/specificity/PPV/NPV of Aspergillus IgG LFA was 65.1%/97.5%/95.4%/78.0%. The sensitivity and specificity of Aspergillus IgG LFA were equivalent to those of Aspergillus IgG ELISA with a 120 AU/mL cut-off, but exhibited significantly higher specificity (97.5% vs 87.5%, P = 0.021) compared to the ELISA with an 80 AU/mL cut-off. The consistency was strong among the two methods (P < 0.001, Kappa = 0.67/0.68). The sensitivities/specificities/PPVs/NPVs of Aspergillus IgG LFA were 57.6%/97.5%/90.5%/84.8% for patients with acute IA, and 73.3%/97.5%/91.7%/90.7% for patients with subacute IA, respectively. The "any-positive" strategy, which combined Aspergillus IgG LFA with sputum culture and serum galactomannan (GM), had a sensitivity/specificity/PPV/NPV of 81.1%/94.7%/95.6%/78.3%. The sensitivity/specificity/PPV/NPV of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) GM was 65.0%/90.0%/92.9%/56.3%. When combined Aspergillus IgG LFA with BALF GM, the figures were 87.5%/85.0%/92.1%/77.3%.
Conclusions: Compared to the Aspergillus IgG ELISA, the Aspergillus IgG LFA exhibits comparable or superior diagnostic efficiency in IA patients, while offering a faster and more convenient option for clinical diagnosis. The "any-positive" strategy of combined diagnosis with Aspergillus IgG LFA serves as a valuable supplement to current diagnostic approaches, particularly benefiting patients who cannot tolerate invasive bronchoscopic procedures.
Keywords: acute invasive aspergillosis; aspergillus IgG lateral flow assay; diagnosis; non-neutropenic patients; subacute invasive aspergillosis.
Copyright © 2025 Lu, Zhong, Wang, Sun, Li, Cai, Cai, Wang, Zhong and Su.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diagnostic Value of Microscopy, Galactomannan, and PCR in Aspergillus Culture-Positive BALF Samples: A Laboratory-Based Pilot Study.Mycoses. 2025 Aug;68(8):e70103. doi: 10.1111/myc.70103. Mycoses. 2025. PMID: 40765325 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of mp-tNGS in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid for the Diagnosis of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Nonneutropenic Patients.J Infect Dis. 2025 Jul 11;231(6):1609-1618. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaf044. J Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39829032
-
Multicenter validation of a galactomannan chemiluminescence immunoassay for the diagnosis of pulmonary aspergillosis on serum of patients with hematological disease.J Clin Microbiol. 2025 Feb 19;63(2):e0105324. doi: 10.1128/jcm.01053-24. Epub 2025 Jan 21. J Clin Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39835823 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody tests for identification of current and past infection with SARS-CoV-2.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 17;11(11):CD013652. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013652.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36394900 Free PMC article.
-
Galactomannan detection for invasive aspergillosis in immunocompromized patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Oct 8;(4):CD007394. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007394. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Dec 30;(12):CD007394. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007394.pub2. PMID: 18843747 Updated.
References
-
- Alhan O., Saba R., Akalin E. H., Ener B., Ture Yuce Z., Deveci B., et al. (2023). Diagnostic efficacy of Aspergillus galactomannan lateral flow assay in patients with hematological Malignancies: A prospective multicenter study. Mycopathologia 188, 643–653. doi: 10.1007/s11046-023-00749-7, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bassetti M., Giacobbe D. R., Agvald-Ohman C., Akova M., Alastruey-Izquierdo A., Arikan-Akdagli S., et al. (2024). Invasive Fungal Diseases in Adult Patients in Intensive Care Unit (FUNDICU): 2024 consensus definitions from ESGCIP, EFISG, ESICM, ECMM, MSGERC, ISAC, and ISHAM. Intensive Care Med. 50, 502–515. doi: 10.1007/s00134-024-07341-7, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

