Agptools: a utility suite for editing genome assemblies
- PMID: 40622245
- PMCID: PMC12286700
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaf388
Agptools: a utility suite for editing genome assemblies
Abstract
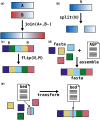
Summary: The AGP format is a tab-separated table format describing how components of a genome assembly fit together. A standard submission format for genome assemblies is a fasta file giving the sequence of contigs along with an AGP file showing how these components are assembled into larger pieces like scaffolds or chromosomes. For this reason, many scaffolding software pipelines output assemblies in this format. However, although many programs for assembling and scaffolding genomes read and write this format, there is currently no published software for making edits to AGP files when performing assembly curation. We present agptools, a suite of command-line programs that can perform common operations on AGP files, such as breaking and joining sequences, inverting pieces of assembly components, assembling contigs into larger sequences based on an AGP file, and transforming between coordinate systems of different assembly layouts. Additionally, agptools includes an API that writers of other software packages can use to read, write, and manipulate AGP files within their own programs.
Availability and implementation: Source code and binaries freely available for download at https://github.com/WarrenLab/agptools, implemented in Python and supported on all operating systems.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
References
-
- AGP Specification v2.1. screed: a simple read-only sequence database, designed for short reads. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/genome\_agp\_specification/ (3 July 2025, date last accessed).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

