Remyelination of chronic demyelinated lesions with directly induced neural stem cells
- PMID: 40622272
- PMCID: PMC12493045
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awaf208
Remyelination of chronic demyelinated lesions with directly induced neural stem cells
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Remyelination of chronic demyelinated lesions with directly induced neural stem cells.Brain. 2025 Oct 3;148(10):e94. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaf274. Brain. 2025. PMID: 41042540 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
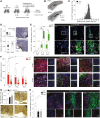
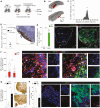
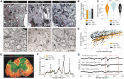
The limited ability of CNS progenitor cells to differentiate into oligodendrocytes limits the repair of demyelinating lesions and contributes to the disability of people with progressive multiple sclerosis (PMS). Neural stem cell (NSC) transplantation has emerged as a safe therapeutic approach in people with PMS, where it holds the promise of healing the injured CNS. However, the mechanisms by which NSC grafts could promote CNS remyelination need to be carefully assessed before their widespread clinical adoption. In this study, we used directly induced NSCs (iNSCs) as a novel transplantation source to boost remyelination in the CNS. Using a mouse model of focal lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC)-induced demyelination, we found that mouse iNSCs promote remyelination by enhancing endogenous oligodendrocyte progenitor cells differentiation and by directly differentiating into mature oligodendrocytes. Transplantation of mouse iNSCs in LPC-lesioned Olig1-/- mice, which exhibits impaired remyelination, confirmed the direct remyelinating ability of grafts and the formation of new exogenous myelin sheaths. We also demonstrated that the xenotransplantation of human iNSCs (hiNSCs) is safe in mice, with hiNSCs persisting long-term in demyelinating lesions where they can produce graft-derived human myelin. Our findings support the use of NSC therapies to enhance remyelination in chronic demyelinating disorders, such as PMS.
Keywords: demyelination; iNSC grafts; multiple sclerosis; oligodendrocyte progenitor cells; remyelination; transplantation.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Conflict of interest statement
S.P. is founder, CSO and shareholder (>5%) of CITC Ltd. The other authors report no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Graves JS, Krysko KM, Hua LH, Absinta M, Franklin RJM, Segal BM. Ageing and multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2023;22:66–77. - PubMed
-
- Franklin RJM. Why does remyelination fail in multiple sclerosis? Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002;3:705–714. - PubMed
-
- Leone MA, Gelati M, Profico DC, et al. Phase I clinical trial of intracerebroventricular transplantation of allogeneic neural stem cells in people with progressive multiple sclerosis. Cell Stem Cell. 2023;30:1597–1609.e8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- PI23/01037/University of Milano-Bicocca
- MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/K026666/1/UK Regenerative Medicine Platform
- FG-2008-36954/MSS_/Multiple Sclerosis Society/United Kingdom
- G105713/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- JR20/00033/MSS_/Multiple Sclerosis Society/United Kingdom
- 2014/PMS/4/AISM
- Italian Ministry of Health
- G118541/MSS_/Multiple Sclerosis Society/United Kingdom
- CB06/05/1131/MSS_/Multiple Sclerosis Society/United Kingdom
- RG79423/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G104956/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- Italian Ministry of University and Research
- MR/K026682/1/UK Regenerative Medicine Platform
- 203151/Z/16/Z/Adelson Medical Research Foundation
- Austrian Science Fund
- CIPROM/2023/053/MSS_/Multiple Sclerosis Society/United Kingdom
- PI23/01037/MSS_/Multiple Sclerosis Society/United Kingdom
- RFA-2203-39318/National Multiple Sclerosis Society
- RD24/0014/0009/MSS_/Multiple Sclerosis Society/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

