Unlocking potent anti-tuberculosis natural products through structure-activity relationship analysis
- PMID: 40622557
- PMCID: PMC12234934
- DOI: 10.1007/s13659-025-00529-4
Unlocking potent anti-tuberculosis natural products through structure-activity relationship analysis
Abstract
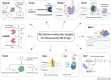
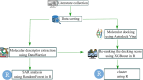
Tuberculosis (TB) remains a world health problem due to the high number of affected individuals, high mortality rates, prolonged treatment durations, and the increasing prevalence of resistance to commercial TB drugs. The emergence of resistance to anti-TB drugs has necessitated urgent research into drug discovery and development, focusing on novel mechanisms of action against Mycobacterium tuberculosis resistant strains. Natural products, with their remarkable structural diversity and bioactivity, are promising sources for the development of new TB drugs or the identification of potential chemical scaffolds exhibiting potent and novel biological activity with minimal or no cytotoxicity to host cells. This review focuses on potent anti-TB natural products with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values below 5 µg mL-1 and examines their structure-activity relationship (SAR). Significant characteristics and relevant biological properties of each compound were analysed using a Random Forest, machine learning algorithm, to explore SAR. Using molecular docking, AutoDock Vina was utilised to assess molecular interactions with protein targets, and predictive accuracy was enhanced using the XGBoost machine learning model. These analyses provide insights into the mode of action of these compounds and help identify key structural features contributing to their anti-TB activity. In addition, this review examines the correlation between the potency of selected anti-TB compounds and their cytotoxicity, offering valuable insights for the identification of promising scaffolds in TB drug discovery.
Keywords: Anti-TB scaffold; Natural Products; Structure–activity relationship; Tuberculosis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: None of the authors of this article has performed studies involving animals in this article. Therefore, ethical declaration is not applicable for this work. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Rapid molecular tests for tuberculosis and tuberculosis drug resistance: a qualitative evidence synthesis of recipient and provider views.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Apr 26;4(4):CD014877. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014877.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35470432 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review on natural products with antimicrobial potential against WHO's priority pathogens.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Jul 1;30(1):525. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02717-x. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40597250 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Type II Diabetes Inhibitors from Genus Daphne Plant-species: An Integrated Computational Study.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025;28(8):1413-1442. doi: 10.2174/0113862073262227231005074024. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025. PMID: 38584562
-
A systematic review of rapid diagnostic tests for the detection of tuberculosis infection.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Jan;11(3):1-196. doi: 10.3310/hta11030. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17266837
-
Health professionals' experience of teamwork education in acute hospital settings: a systematic review of qualitative literature.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Apr;14(4):96-137. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-1843. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532314
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

