Predictive factors at initial visit for sunset glow fundus in Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease
- PMID: 40624077
- PMCID: PMC12234651
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-08252-3
Predictive factors at initial visit for sunset glow fundus in Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease
Abstract
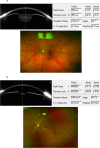
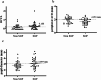
This study aimed to identify factors present at the initial visit for the development of sunset glow fundus (SGF) in Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada (VKH) disease. A total of 139 eyes from 70 naïve patients with acute VKH disease who underwent pulse steroid therapy were categorized into "SGF" and "non-SGF" groups based on fundus appearance at 12 months post-therapy. Multivariable analysis revealed that patients with meningismus (p = 0.004), incomplete type (p = 0.035), and probable type (p = 0.002) in older revised diagnostic criteria; ex-smoker (p = 0.016), and smoker (p = 0.010) status; high logarithmic best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) (p < 0.001); high spherical equivalent (SE) (p = 0.005); shallow peripheral anterior chamber depth (ACD) (p < 0.001); narrow anterior chamber angle (ACA) (p = 0.015); increased pupil diameter (p < 0.001); and thicker cornea (p = 0.019) were associated with SGF. The optimal cut-off values for predicting SGF were identified as follows: logarithmic BCVA greater than 0.261, SE exceeding - 2.813 D, peripheral ACD less than 2.138 mm, ACA less than 40.55 °, pupil diameter exceeding 3.040 mm, and corneal thickness exceeding 579.500 μm. Patients with VKH disease who exhibit above risk factors require early and careful management.
Keywords: Corneal thickness; Pupil diameter; Sunset glow fundus; Visual acuity; Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada disease.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

