AI driven automation for enhancing sustainability efforts in CDP report analysis
- PMID: 40624129
- PMCID: PMC12234670
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-07584-4
AI driven automation for enhancing sustainability efforts in CDP report analysis
Abstract
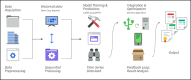
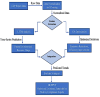
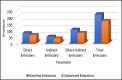
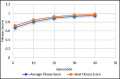
The need for sustainable practices in supply chains is becoming increasingly critical, as businesses face pressure to reduce their carbon footprint while maintaining operational efficiency. This paper proposes a novel hybrid approach that combines Genetic Algorithms (GA) with Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks to optimize supply chain sustainability. The proposed system leverages publicly available Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP)-reported data to predict emissions and optimize resource allocation. The primary objective of this research is to develop a cost-effective, scalable solution that reduces emissions, improves operational efficiency, and ensures regulatory compliance within supply chains. The hybrid model consists of two main components: LSTM networks for predictive modeling of emission trends and GA for optimization of supply chain processes. LSTM is used to forecast future emissions based on historical data, while GA optimizes resource management, including transportation choices and energy consumption, to minimize emissions and operational costs. The system employs a multi-objective optimization approach, addressing the simultaneous goals of emission reduction, operational efficiency, and compliance with environmental regulations. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach. A 23.67% reduction in total emissions was achieved, with the most significant improvements in indirect emissions. The system also improved operational efficiency by 10.98%, while ensuring 100% compliance with environmental regulations, eliminating any penalties. The hybrid GA-LSTM framework offers valuable insights for businesses seeking to meet sustainability targets and provides a practical, data-driven method for improving supply chain performance. The proposed system is not only applicable to large corporations but can also be scaled for use in small and medium-sized enterprises, offering a pathway for widespread adoption of sustainable practices across industries.
Keywords: Carbon disclosure project; Emissions optimization; Genetic algorithm; Long short-term memory; Resource efficiency; Sustainability.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Consent for publication: All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome.2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31613449 Free Books & Documents.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Accreditation through the eyes of nurse managers: an infinite staircase or a phenomenon that evaporates like water.J Health Organ Manag. 2025 Jun 30. doi: 10.1108/JHOM-01-2025-0029. Online ahead of print. J Health Organ Manag. 2025. PMID: 40574247
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
References
-
- Cordero, D., Juiz, C., Mory, A., Bermeo, V. & Andrade, D. Model for the intent to adopt green IT in the context of organizations. IEEE Access10, 65636–65657. 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3184727 (2022).
-
- Akhtar, I., Kirmani, S., Jameel, M. & Alam, F. Feasibility analysis of solar technology implementation in restructured power sector with reduced carbon footprints. IEEE Access9, 30306–30320. 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3059297 (2021).
-
- Savazzi, S., Rampa, V., Kianoush, S. & Bennis, M. An energy and carbon footprint analysis of distributed and federated learning. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw.7(1), 248–264. 10.1109/TGCN.2022.3186439 (2023).
-
- González-González, J., García-Méndez, S., De Arriba-Pérez, F., González-Castaño, F. J. & Barba-Seara, Ó. Explainable automatic industrial carbon footprint estimation from bank transaction classification using natural language processing. IEEE Access10, 126326–126338. 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3226324 (2022).
-
- Hans, M., Hikmawati, E. & Surendro, K. Predictive analytics model for optimizing carbon footprint from students’ learning activities in computer science-related majors. IEEE Access11, 114976–114991. 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3324725 (2023).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

