Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes improve vascular remodeling by inhibiting EGFR/ErbB2 heterodimerization in hypoxic pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 40624204
- PMCID: PMC12234707
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-09333-z
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes improve vascular remodeling by inhibiting EGFR/ErbB2 heterodimerization in hypoxic pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
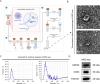
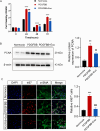
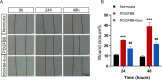
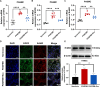
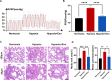
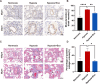
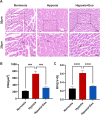
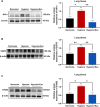
A key characteristic of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension (HPH) is pulmonary vascular remodeling, involving abnormal proliferation and migration of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs). Recent studies indicate that mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (MSC-exo) exhibit therapeutic effects on HPH. MSC-exosomes were isolated from the conditioned medium of bone mesenchymal stem cells using ultracentrifugation, confirmed via Western blotting (WB), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and nanoparticle tracking analyses (NTA). Platelet-derived growth factor BB (PDGFBB) induced pathological behavior in PASMCs, replicating the conditions observed in HPH. HPH rats were subjected to a low oxygen environment (10 ± 1% oxygen) for 8 h daily over 28 days. Parameters such as right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP), right ventricular hypertrophy index (RVHI), and pulmonary vascular remodeling were evaluated. MSC-exosomes suppressed PDGFBB-induced proliferation and migration of PASMCs. Additionally, MSC-exosomes protected rats from hypoxia-induced increases in RVSP, right ventricular hypertrophy, and pulmonary vascular remodeling. The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and Erb-B2 receptor tyrosine kinase 2 (ErbB2) was investigated in both HPH lung tissues and PDGFBB-induced PASMCs. Results indicated significant upregulation of EGFR/ErbB2 expression in HPH and PDGFBB-induced PASMCs, which was suppressed by MSC-exosomes. The study demonstrates that MSC-exosomes inhibit the development of HPH by suppressing excessive proliferation and migration of PASMCs through the inhibition of EGFR/ErbB2 heterodimerization.
Keywords: Epidermal growth factor receptor; Erb-B2 receptor tyrosine kinase 2; Hypoxic pulmonary hypertension; Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes; Pulmonary vascular remodeling.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics statement: All animal experiments received approval from the Animal Ethics Committee of Soochow University (20220201A0303) and were conducted according to their established guidelines. The use of animals and experimental procedures strictly adhered to international ethical standards and the National Institutes of Health’s guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals. Our research involving live animals is conducted in accordance with the ARRIVE guidelines.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tibetan mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes alleviate pulmonary vascular remodeling in hypoxic pulmonary hypertension rats.Stem Cells. 2024 Aug 1;42(8):720-735. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxae032. Stem Cells. 2024. PMID: 38717187
-
Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stromal cells exert a therapeutic effect on hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension by modulating the YAP1/SPP1 signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Dec;168:115816. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115816. Epub 2023 Nov 2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37918254
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorate hypoxic pulmonary hypertension by inhibiting the Hsp90aa1/ERK/pERK pathway.Biochem Pharmacol. 2024 Aug;226:116382. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116382. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Biochem Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38909785
-
Mesenchymal Stem-Cell-Derived Exosomes and MicroRNAs: Advancing Cell-Free Therapy in Systemic Sclerosis.Cells. 2025 Jul 3;14(13):1018. doi: 10.3390/cells14131018. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40643538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a potential therapeutic strategy for ferroptosis.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Jul 15;16(1):368. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04511-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40660292 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yang, L., Liang, H., Shen, L., Guan, Z. & Meng, X. LncRNA Tug1 involves in the pulmonary vascular remodeling in mice with hypoxic pulmonary hypertension via the microRNA-374c-mediated Foxc1. Life Sci.237, 116769. 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116769 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Waypa, G. B. & Schumacker, P. T. Roles of HIF1 and HIF2 in pulmonary hypertension: it all depends on the context. Eur. Respir. J.5410.1183/13993003.01929-2019 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Li, Y. et al. MicroRNA-150 relieves vascular remodeling and fibrosis in hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Biomed. Pharmacother. 109, 1740–1749. 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.11.058 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

