Development of postbiotic supplemented polylactic acid films for improving quality and shelf life of rainbow trout
- PMID: 40624225
- PMCID: PMC12234849
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-09249-8
Development of postbiotic supplemented polylactic acid films for improving quality and shelf life of rainbow trout
Abstract
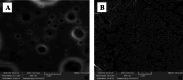
Bioactive metabolites derived from lactic acid bacteria (LAB), commonly referred to as postbiotics, have recently attracted increasing interest in the realm of food packaging. In the present study, biopolymeric films incorporated with postbiotics of Lactococcus lactis were produced using polylactic acid (PLA). The fabricated films were characterized in terms of physicochemical, optical, mechanical, structural, and morphological characteristics. Additionally, the effect of the coating on the quality and shelf life of rainbow trout fillets during the seventh day of refrigerated storage was examined. The findings indicated that the values of pH, °Brix, and antioxidant activity, as measured by the DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) radical scavenging assay, were 4.57, 4.80, and 39.29%, respectively. Furthermore, the film incorporated with postbiotic (PLA-POST) exhibited no antibacterial activity against the tested pathogens. Treatment of the films with postbiotic resulted in increased values of thickness, moisture content, turbidity, a*, b*, ΔE*, and elongation at the breakpoint compared to the PLA films. The functional groups and chemical bonds of PLA and PLA-POST films were recorded using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Moreover, thermal analysis indicated that the supplementation of postbiotics enhanced the thermal stability of the films (p < 0.05). Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) micrographs of films also revealed that the addition of postbiotics created a rougher appearance with microclusters. In the study, a postbiotic coating for fish fillets was also developed. During refrigerated storage, no differences were found in color, microbiological, and sensory characteristics among the fish samples (p > 0.05). In conclusion, the development of active biodegradable films incorporating postbiotics indicates a promising alternative to traditional petroleum-based packaging materials. Importantly, the use of postbiotics to coat food products, particularly seafood, has demonstrated minimal effects on the sensory characteristics, maintaining their natural flavor, texture, and overall acceptability.
Keywords: Chilled storage; Film and coating; Fish fillets; Physicochemical characteristics; Postbiotic.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Antioxidant Films of Starch Blends With Onion Peel Extract for Packaging Coriander.J Food Sci. 2025 Jul;90(7):e70383. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.70383. J Food Sci. 2025. PMID: 40635165
-
Effects of supplementation of live and heat-treated Bifidobacterium animalis subspecies lactis CECT 8145 on glycemic and insulinemic response, fecal microbiota, systemic biomarkers of inflammation, and white blood cell gene expression of adult dogs.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae291. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae291. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 39320367
-
Evaluation of alginate-based coatings enriched with postbiotics from Bifidobacterium spp. on the quality and safety of Turkey meat.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):23634. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09913-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40604258 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Costello, C. et al. The future of food from the sea. Nature588, 95–100 (2020). - PubMed
-
- FAO, F & Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The state of world fisheries and aquaculture 2018—Meeting the sustainable development goals. CC BYNC-SA 3 (2018). (2018).
-
- Elhami, B., Farahani, S. S. & Marzban, A. Improvement of energy efficiency and environmental impacts of rainbow trout in Iran. Artif. Intell. Agric.2, 13–27 (2019).
-
- Gupta, R. K., Guha, P. & Srivastav, P. P. Natural polymers in bio-degradable/edible film: A review on environmental concerns, cold plasma technology and nanotechnology application on food packaging—A recent trends. Food Chem. Adv.1, 100135 (2022).
-
- İncili, G. K. et al. Whole-cell postbiotics: An innovative approach for extending the shelf life and controlling major foodborne pathogens in chicken breast fillets. Food Bioprocess Technol.16, 1502–1524 (2023).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

