TERRA R-loops trigger a switch in telomere maintenance towards break-induced replication and PRIMPOL-dependent repair
- PMID: 40624280
- PMCID: PMC12361433
- DOI: 10.1038/s44318-025-00502-4
TERRA R-loops trigger a switch in telomere maintenance towards break-induced replication and PRIMPOL-dependent repair
Abstract
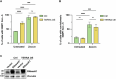
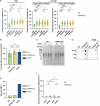
TERRA long noncoding RNAs associate with telomeres post transcription through base-pairing with telomeric DNA forming R-loop structures. TERRA regulates telomere maintenance but its exact modes of action remain unknown. Here, we induce TERRA transcription and R-loop formation in telomerase-expressing cells and determine that TERRA R-loop formation requires non-redundant functions of the RAD51 DNA recombinase and its enhancer RAD51AP1. TERRA R-loops interfere with semiconservative DNA replication, promoting telomere maintenance by a homology-directed repair (HDR) mechanism known as break-induced replication (BIR), which ensures telomere maintenance in ALT cancer cells. In addition, TERRA induces PRIMPOL-dependent repair, which can initiate DNA synthesis de novo downstream of replication obstacles. PRIMPOL acts in parallel to BIR for telomere maintenance of TERRA-overexpressing cells, promoting their survival. Similarly, we find that PRIMPOL depletion is synthetic-lethal with BIR deficiency in U2OS ALT cancer cells. Therefore, TERRA R-loops by themselves are sufficient to induce ALT-typical telomere repair mechanisms, in the absence of other ALT-typical telomeric chromatin changes.
Keywords: Break-induced Replication; PRIMPOL; R-loops; TERRA; Telomeres.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Aguilera A, Ruzov A (eds) (2022) R-Loops: methods and protocols. Springer US, New York, NY
-
- Azzalin CM, Reichenbach P, Khoriauli L, Giulotto E, Lingner J (2007) Telomeric repeat containing RNA and RNA surveillance factors at mammalian chromosome ends. Science 318:798–801 - PubMed
-
- Bailey SM, Goodwin EH, Meyne J, Cornforth MN (1996) CO-FISH reveals inversions associated with isochromosome formation. Mutagenesis 11:139–144 - PubMed
-
- Barde I, Salmon P, Trono D (2010) Production and titration of lentiviral vectors. Curr Protoc Neurosci 53:4.21.1–4.21.23 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

