Multi-omics analysis of the effects of pla2g4a on the prognosis of various cancers and its experimental validation in breast cancer cell lines
- PMID: 40624348
- PMCID: PMC12234970
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-03118-6
Multi-omics analysis of the effects of pla2g4a on the prognosis of various cancers and its experimental validation in breast cancer cell lines
Abstract
Background: Platelet-related exosomes (PREs) are microparticles secreted by platelets into the bloodstream and are implicated in various cancer processes. This study aims to identify critical genes involved in Breast Cancer (BC)-associated PREs and to evaluate their role in cancer prognosis. PLA2G4A was identified as a key gene through the use of machine learning techniques and various genomic analyses, providing a foundation for precision medicine in BC treatment.
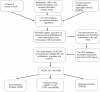
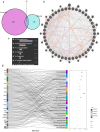
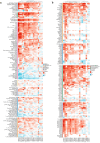
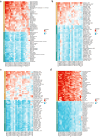
Methods: Download cancer-related data from databases such as UCSC Xena and ExMdb, use LASSO Cox regression and various machine learning algorithms to screen genes associated with BC survival, and perform functional and pathway enrichment analysis. The expression, immune relevance, diagnostic efficacy, and drug sensitivity of the PLA2G4A gene in pan-cancer and BC were specifically analyzed. The function of PLA2G4A in BC was validated through experiments, and its drug response and molecular docking were predicted using various databases and software tools.
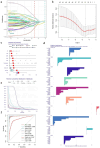
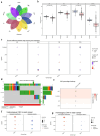
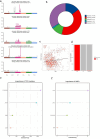
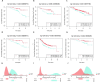
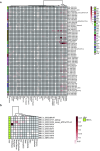
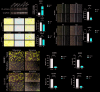
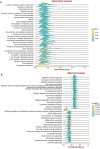
Results: Machine learning methods and LASSO Cox regression were applied to analyze the relationship between gene expression and BC survival. PLA2G4A was identified as a key gene associated with cancer prognosis, supported by analyses of differential gene expression, survival outcomes, single nucleotide variations (SNVs), and copy number variations (CNVs). Biological pathway analyses through KEGG, GO, and GSEA highlighted PLA2G4A's involvement in key cancer-related processes. In vitro studies, including cell scratch assays, Transwell migration assays, and EdU proliferation tests, demonstrated that overexpression of PLA2G4A inhibited the proliferation and migration of BC cells.
Conclusions: PLA2G4A plays a crucial role in the progression of BC, acting as a potential tumor-suppressor gene. The findings support its potential as a prognostic biomarker and further investigation is needed to explore its therapeutic potential in clinical settings.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Breast neoplasm; Cancer; Machine learning; PLA2G4A; Platelet-related exosomes.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Burstein HJ, Curigliano G, Thürlimann B, Weber WP, Poortmans P, Regan MM, et al. Customizing local and systemic therapies for women with early breast cancer: the St. Gallen International Consensus Guidelines for treatment of early breast cancer 2021. Ann Oncol. 2021;32(10):1216–35. 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.06.023. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gradishar WJ, Moran MS, Abraham J, Aft R, Agnese D, Allison KH et al. Breast cancer, version 3.2022, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. JNCCN. 2022;20(6):691–722. 10.6004/jnccn.2022.0030. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
