Integrating Machine Learning into Myositis Research: a Systematic Review
- PMID: 40624382
- PMCID: PMC12234630
- DOI: 10.1007/s12016-025-09076-9
Integrating Machine Learning into Myositis Research: a Systematic Review
Abstract
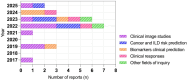
Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) are a group of autoimmune rheumatic diseases characterized by proximal muscle weakness and extra muscular manifestations. Since 1975, these IIM have been classified into different clinical phenotypes. Each clinical phenotype is associated with a better or worse prognosis and a particular physiopathology. Machine learning (ML) is a fascinating field of knowledge with worldwide applications in different fields. In IIM, ML is an emerging tool assessed in very specific clinical contexts as a complementary tool for research purposes, including transcriptome profiles in muscle biopsies, differential diagnosis using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and ultrasound (US). With the cancer-associated risk and predisposing factors for interstitial lung disease (ILD) development, this systematic review evaluates 23 original studies using supervised learning models, including logistic regression (LR), random forest (RF), support vector machines (SVM), and convolutional neural networks (CNN), with performance assessed primarily through the area under the curve coupled with the receiver operating characteristic (AUC-ROC).
Keywords: Clinical prediction; Image analysis; Machine learning; Myositis; Treatment responses.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics Approval: The manuscript was not submitted to other journals for consideration. The submitted work is a review with no plagiarism. The results are presented clearly, honestly, and without fabrication, falsification, or inappropriate data manipulation. No data, text, or theories by others are presented as if they were the author’s own. Proper acknowledgements are given to the cited works. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mortality Risk Prediction in Patients With Antimelanoma Differentiation-Associated, Gene 5 Antibody-Positive, Dermatomyositis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease: Algorithm Development and Validation.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Feb 5;27:e62836. doi: 10.2196/62836. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 39908093 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of adult-onset clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis (dermatomyositis siné myositis): a missing link within the spectrum of the idiopathic inflammatory myopathies.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006 Apr;54(4):597-613. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2005.10.041. Epub 2006 Jan 23. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006. PMID: 16546580
-
Proposal for Using AI to Assess Clinical Data Integrity and Generate Metadata: Algorithm Development and Validation.JMIR Med Inform. 2025 Jun 30;13:e60204. doi: 10.2196/60204. JMIR Med Inform. 2025. PMID: 40587839 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of clinical and serological biomarkers in a nomogram for predicting interstitial lung disease in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies.BMC Rheumatol. 2025 Jul 1;9(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s41927-025-00534-7. BMC Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40598457 Free PMC article.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
References
-
- Dalakas MC (2023) Autoimmune inflammatory myopathies. pp 425–460. 10.1016/b978-0-323-98818-6.00023-6
-
- Hoogendijk JE, Amato AA, Lecky BR et al (2004) 119th ENMC international workshop: trial design in adult idiopathic inflammatory myopathies, with the exception of inclusion body myositis, 10–12 October 2003, Naarden, The Netherlands. Neuromuscul Disord 14:337–345. 10.1016/j.nmd.2004.02.006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- CF-2023-G-1396/Secretaría de Ciencias, Humanidades y Tecnologías (SECIHTI)
- CF-2023-G-1396/Secretaría de Ciencias, Humanidades y Tecnologías (SECIHTI)
- CF-2023-G-1396/Secretaría de Ciencias, Humanidades y Tecnologías (SECIHTI)
- CF-2023-G-1396/Secretaría de Ciencias, Humanidades y Tecnologías (SECIHTI)
- CF-2023-G-1396/Secretaría de Ciencias, Humanidades y Tecnologías (SECIHTI)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical