Safety comparison of mRNA, viral vector, and inactivated Covid-19 vaccines: incidence of adverse events following primary and booster doses among medical professionals in Malaysia
- PMID: 40624462
- PMCID: PMC12232647
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-025-11254-1
Safety comparison of mRNA, viral vector, and inactivated Covid-19 vaccines: incidence of adverse events following primary and booster doses among medical professionals in Malaysia
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to examine adverse events following first, second, and booster doses of Covid-19 vaccines in Malaysia.
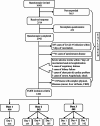
Methods: This was a prospective longitudinal cohort study conducted between September 2021 to September 2022. Recipients who received different Covid-19 vaccines (Comirnaty, Vaxzevria, and CoronaVac) completed a self-report questionnaire of adverse events on days 1, 2, 4, and 7 following their primary (first and second) and booster (third) vaccinations.
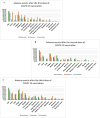
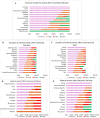
Results: A total of 1283 respondents had completed the questionnaire survey. The most frequent adverse events among Comirnaty recipients (n = 271) following the first dose were pain (87.4%), fatigue (56.9%), myalgia (37.2%), and fever (17.5%), which further increased to 92.1%, 72.8%, 51·2%, and 48%, respectively, following the booster. The most frequent adverse events following the first dose of Vaxzevria (n = 90) were pain (84.4%), fever (76.7%), headache (58.9%) and myalgia (53.3%). Adverse events were reduced after the second dose of Vaxzevria but sharply increased after the booster. The most common adverse events among CoronaVac recipients (1st dose) were pain at the injection site (69.1%), fatigue (49.1%) and increased hunger (34.5%). However, adverse events subsequently decreased after the second and booster doses. The average number of adverse events was highest for Vaxzevria after the first dose (n = 6) and booster dose (n = 6) and lowest for CoronaVac after the first (n = 3), second (n = 2) and booster doses (n = 2).
Conclusion: The incidence of adverse events following the first dose of the Covid-19 vaccine was highest among Vaxzevria recipients. Adverse events following Comirnaty vaccine increased gradually from primary to booster dose, whereas recipients with CoronaVac showed subsequent lesser adverse events following primary and booster doses.
Keywords: Adverse events; Booster dose; Comparative study; Covid-19 vaccines; Inactivated viral vaccine; Vaccine safety; Viral vectored vaccine; mRNA vaccine.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis of humoral immunity kinetics following three COVID-19 vaccines in a multi-ethnic cohort of medical students and healthcare professionals across Malaysia.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21953. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07895-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595319 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of adverse events and comorbidity exacerbation following the COVID-19 booster dose: A national survey among randomly-selected booster recipients.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 11;20(7):e0326231. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0326231. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40644466 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of vaccine booster doses on specific B- and T-lymphocyte dynamics in Thai healthcare personnel following COVID-19 vaccination.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 16;15(1):25713. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-10400-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40670524 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of COVID-19 vaccines.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Dec 7;12(12):CD015477. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015477. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36473651 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the Effectiveness and Safety of Heterologous Booster Doses with Homologous Booster Doses for SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Aug 29;19(17):10752. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191710752. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36078466 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Worldometer. Malaysia COVID - Coronavirus Statistics. Available from: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/country/malaysia/
-
- World Health Organization. The different types of COVID-19 vaccines. 2021 Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/the-race-for-a-Covi...
-
- Ministry of Health Malaysia. Clinical guidelines on COVID-19 vaccination in Malaysia, 4th edition. 2021 Available from: https://www.moh.gov.my
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

