Assessment of decisional capacity. A systematic review and analysis of instruments regarding their applicability to requests for assisted suicide
- PMID: 40624666
- PMCID: PMC12260724
- DOI: 10.1192/j.eurpsy.2025.10041
Assessment of decisional capacity. A systematic review and analysis of instruments regarding their applicability to requests for assisted suicide
Abstract
Background: Decisional capacity is an important requirement for assisted suicide, which has been legalized in an increasing number of countries. While several instruments have been developed over the past few decades to assess the capacity to consent to treatment, little is known about their applicability to assessing capacity in the context of requests for assisted suicide.
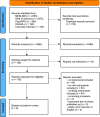
Methods: Systematic review of instruments assessing decisional capacity published up to March 2024. Data concerning criteria for determining decisional capacity, psychometric properties, and other aspects were extracted from all instruments included. Selected instruments were analyzed regarding their applicability to requests for assisted suicide.
Results: We identified 23 instruments assessing the capacity to consent to treatment. There is considerable heterogeneity regarding the criteria utilized for assessing decisional capacity and their operationalization. Next to more cognitive abilities, some instruments directly incorporated emotions and values. Five instruments were assessed for applicability to requests for assisted suicide. The framing of decisional capacity within the context of disease and treatment options frequently limits the application of instruments to assess decisional capacity in the context of requests for assisted suicide.
Conclusions: No instrument could be identified that could be applied to assessing decisional capacity in the context of requests for assisted suicide without any limitations or without necessitating adjustments. Further normative and empirical work is required for developing an instrument that could be applicable in this context.
Keywords: assisted suicide; decisional capacity; instruments; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared none.
Similar articles
-
The measurement of collaboration within healthcare settings: a systematic review of measurement properties of instruments.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Apr;14(4):138-97. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-2159. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532315
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Interventions for supporting pregnant women's decision-making about mode of birth after a caesarean.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jul 30;2013(7):CD010041. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010041.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23897547 Free PMC article.
-
Eliciting adverse effects data from participants in clinical trials.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 16;1(1):MR000039. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000039.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29372930 Free PMC article.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
References
-
- Schweitser F, Stuy J, Distelmans W, Rigo A. Assessment of patient decision-making capacity in the context of voluntary euthanasia for psychic suffering caused by psychiatric disorders: a qualitative study of approaches among Belgian physicians. J Med Ethics. 2021;47:e38. 10.1136/medethics-2019-105690. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous