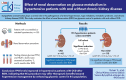
Effect of renal denervation on glucose metabolism in hypertensive patients with and without chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 40625696
- PMCID: PMC12231565
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfaf184
Effect of renal denervation on glucose metabolism in hypertensive patients with and without chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Backgroun: Sympathetic overactivation is associated with numerous pathologies, including arterial hypertension, diabetes, metabolic syndrome and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Renal denervation (RDN) has emerged as an adjacent therapy for the management of hypertension. By modulating sympathetic activity in the whole body, RDN has shown conflicting results regarding insulin secretion and glucose homeostasis. The aim of this study is to analyse the impact of RDN on glycaemic control in patients with CKD.
Methods: A total of 155 hypertensive patients with (n = 45) or without CKD (n = 110) were included in this post hoc analysis. All patients underwent radiofrequency-, ultrasound- or alcohol injection-based RDN. Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and haemoglobin A1c levels were measured at baseline, 3 months and 6 months after RDN in parallel with the office and 24-h ambulatory blood pressure. CKD was defined either by clinical diagnosis, an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 15-59 ml/min/1.73 m2 and/or A2/A3 albuminuria in hypertensive patients, repeatedly confirmed, or several of these criteria.
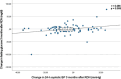
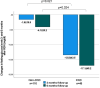
Results: In the total study cohort, FPG decreased by 5.1 ± 29.1 mg/dl (P = .032) and by 7.9 ± 32.7 mg/dl (P = .003) at 3 and 6 months after RDN, respectively. The change in FPG levels was related to the change in 24-h systolic BP (r = 0.286, P = .008) 3 months after RDN. Among patients with CKD, FPG levels decreased by 13.5 ± 43.5 mg/dl at 3 months (P = .043) and by 17.1 ± 45.2 mg/dl at 6 months (P = .015) following RDN. These reductions were greater compared with the non-CKD group (P = .021 and P = .024, respectively). After excluding patients on oral antidiabetic or insulin therapy, patients with CKD (but not those without CKD) exhibited a reduction in FPG levels of 6.7 ± 15.3 mg/dl (P = .043) at 6 months post-RDN. No significant changes were observed in eGFR in either group.
Conclusion: We observed that FPG levels improved to a greater extent in hypertensive patients with CKD after RDN. Thus RDN may have a broader therapeutic impact beyond blood pressure reduction in CKD patients.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; glucose metabolism; renal denervation.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Conflict of interest statement
V.B., D.K., A.S., K.S., M.K., M.S., and M.U. declare that they have no conflicts of interest with respect to this study. R.E.S. reports the following conflicts of interest: institutional grants from Medtronic, Recor Medical, Ablative Solutions, and Sonivie/Boston; speaker and adviser bureau: Medtronic and Recor Medical. A.B. received a travel grant from Recor Medical.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of renal denervation on kidney function in patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Hum Hypertens. 2024 Jan;38(1):29-44. doi: 10.1038/s41371-023-00857-3. Epub 2023 Sep 4. J Hum Hypertens. 2024. PMID: 37666908 Free PMC article.
-
Synbiotics, prebiotics and probiotics for people with chronic kidney disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Oct 23;10(10):CD013631. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013631.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37870148 Free PMC article.
-
Early referral strategies for management of people with markers of renal disease: a systematic review of the evidence of clinical effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and economic analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2010 Apr;14(21):1-184. doi: 10.3310/hta14210. Health Technol Assess. 2010. PMID: 20441712
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers for adults with early (stage 1 to 3) non-diabetic chronic kidney disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jul 19;7(7):CD007751. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007751.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37466151 Free PMC article.
-
Altered dietary salt intake for preventing diabetic kidney disease and its progression.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 16;1(1):CD006763. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006763.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36645291 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous