BRICS sequential therapeutic regimen as first-Line treatment for PD-L1-negative metastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring EGFR/ALK wild-type status: a retrospective study
- PMID: 40625736
- PMCID: PMC12230763
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1618110
BRICS sequential therapeutic regimen as first-Line treatment for PD-L1-negative metastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring EGFR/ALK wild-type status: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Patients with PD-L1-negative, EGFR/ALK wild-type metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) exhibit limited responses to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). This study evaluates the BRICS regimen-a sequential approach combining stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT), probiotics, PD-1 inhibitors, and low-dose chemotherapy-to overcome immunotherapy resistance.
Methods: This retrospective study included 23 patients treated between 2018 to 2024. Eligibility criteria: confirmed PD-L1-negative NSCLC, no actionable mutations, and measurable lesions. The BRICS regimen comprised SBRT (24 Gy in 3 fractions) to a single lesion, oral probiotics (6 g/day), low-dose chemotherapy, and PD-1 inhibitors administered every 21 days for six cycles. Outcomes included objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and safety.
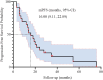
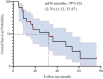
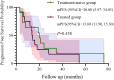
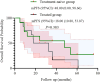
Results: Median age was 62 years; 82.6% were male. ORR and DCR were both 95.7%. Median PFS was 16 months (95% CI: 9.11-22.89), and median OS was 32.7 months (95% CI: 11.53-53.87). In subgroup analysis based on prior treatment status, median PFS and OS were numerically longer in treatment-naïve patients compared to previously treated patients (mPFS: 20.0 vs. 13.6 months; mOS: 48.0 vs. 18.0 months), though without statistical significance (P > 0.05). Poor ECOG performance status predicted poorer PFS (HR=9.908, p=0.013) and OS (HR=26.406, p=0.008). Adverse events were predominantly grade 1 to 2 (fatigue:13.2%, rash:8.7%), with no grade ≥3 toxicities.
Conclusions: The BRICS regimen demonstrated promising efficacy and safety in PD-L1-negative NSCLC, potentially overcoming resistance through multimodal immunomodulation. clinical benefit was observed regardless of treatment line, with a trend toward improved outcomes when administered as first-line therapy. Prospective trials are warranted to validate these findings and explore mechanisms underlying radiotherapy-microbiome-chemotherapy synergy.
Keywords: BRICS regimen; NSCLC; efficacy; first-line treatment; retrospective study.
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Wang, Fang, Wu, Li, Xu, Zhu, Cheng, Yu and Peng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparison of efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 combination therapy in first-line treatment of advanced NSCLC: an updated systematic review and network meta-analysis.Clin Transl Oncol. 2024 Oct;26(10):2488-2502. doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03442-3. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Clin Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38625495
-
Comparison of Efficacy and Safety of Single and Double Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Based First-Line Treatments for Advanced Driver-Gene Wild-Type Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 16;12:731546. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.731546. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34484242 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted therapy for advanced anaplastic lymphoma kinase (<I>ALK</I>)-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jan 7;1(1):CD013453. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013453.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 34994987 Free PMC article.
-
First-line treatment of advanced epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation positive non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 25;(5):CD010383. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010383.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 18;3:CD010383. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010383.pub3. PMID: 27223332 Updated.
-
Atezolizumab and bevacizumab, with or without radiotherapy, versus docetaxel in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer previously treated with a checkpoint inhibitor and chemotherapy: results from the randomized, phase Ib/II MORPHEUS-Lung study.J Immunother Cancer. 2025 Aug 4;13(8):e011892. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2025-011892. J Immunother Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40759444 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

